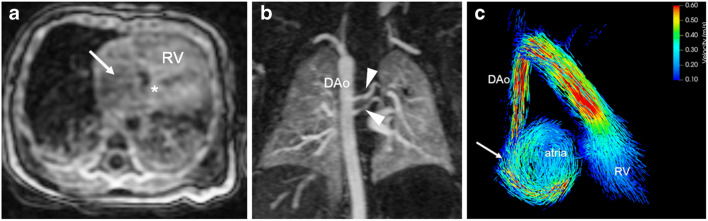
Fig. 11.
Heterotaxy syndrome associated with complete atrioventricular septal defect, insufficiency of the common atrioventricular valves, transposition of the great arteries, pulmonary atresia with non-confluent pulmonary arteries and multiple systemic collateral arteries originating from the descending aorta in a 1-day-old girl. Cardiac MRI was necessary for comprehensive anatomical overview preoperatively. a Axial 4-D flow MRI magnitude image demonstrates the quite impressive quality of 4-D flow raw magnitude images in neonates, resembling that of cine steady-state free precession sequences. It depicts the septal defect (asterisk), the right ventricular dilatation (RV) and a jet (arrow) in the right atrium caused by atrioventricular valve insufficiency. b Coronal MR angiography image shows two small aorto-pulmonary collateral arteries to the left lung (arrowheads) originating from the descending aorta (DAo). c Coronal 4-D flow pathlines reveal flow disturbances in the atria caused by insufficiency of the common atrioventricular valve resulting in a large vortex (arrow). The small aorto-pulmonary collaterals are not visualised