Fig. 6.
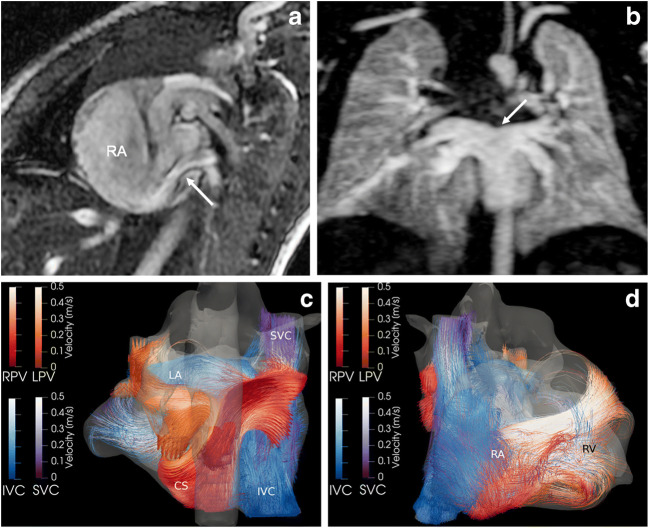
Intracardiac total anomalous venous connection in 7-day-old boy. a Sagittal cine steady-state free precession image (repetition time/echo time 4.2/1.8 ms) reveals the unobstructed pulmonary venous flow via a common confluence and the coronary sinus (arrow) into the dilated right atrium (RA). b Coronal magnetic resonance (MR) angiography maximum-intensity projection depicts the common pulmonary venous drainage (arrow) without obstruction. c, d Posterior (c) and anterior (d) views of 4-D flow-based colour-coded pathline tracking demonstrate the abnormal flow of right (RPV, red) and left (LPV, orange) pulmonary veins entering the right atrium (RA) inferiorly via the coronary sinus (CS). Blood from the inferior caval vein (IVC) flows directly to the left atrium (LA) via an associated atrial septal defect. RV right ventricle, SVC superior caval vein