Figure 1 |. Structure of MFSD2A in an inward-facing conformation.
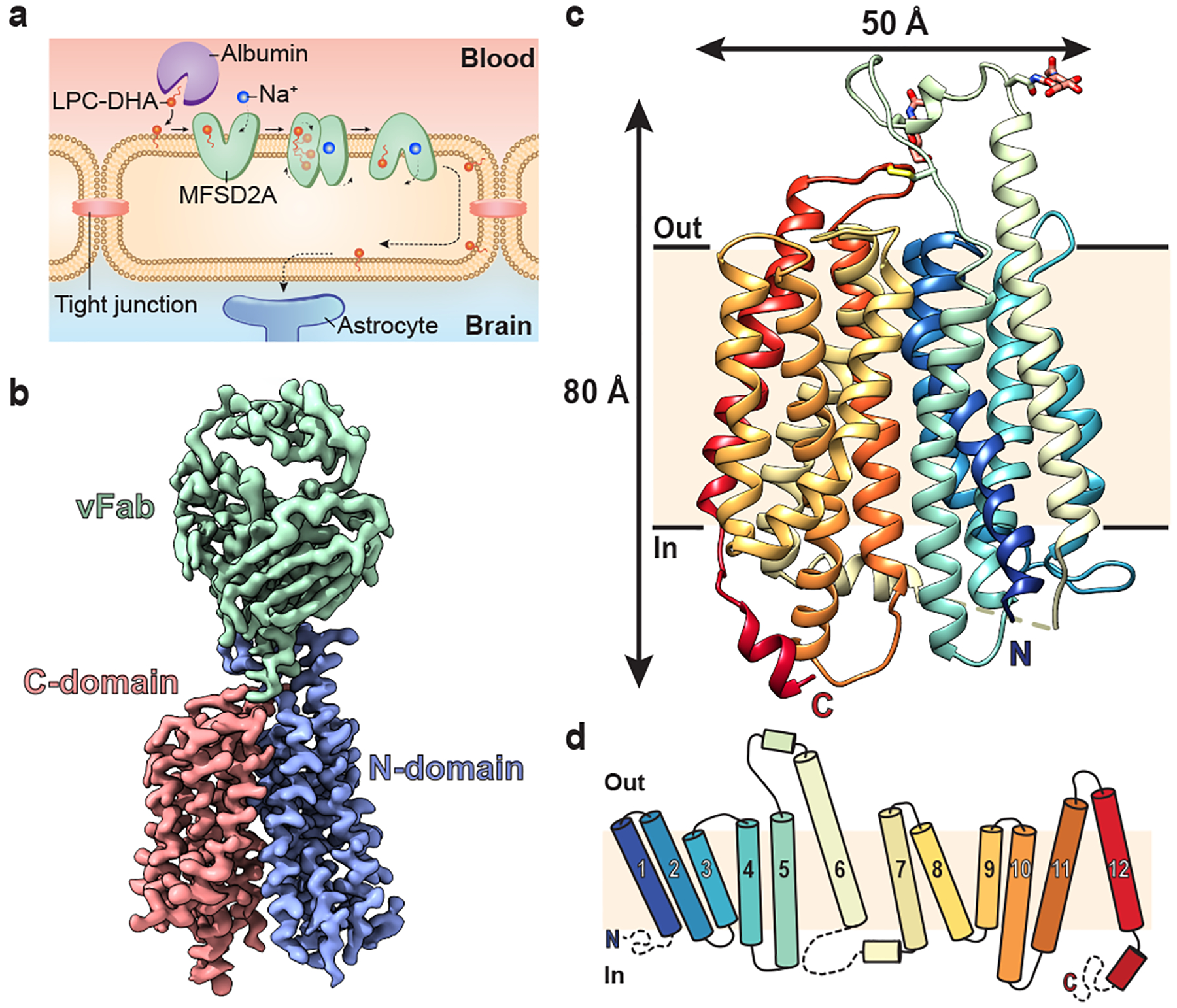
a, Schematic of Na+-dependent, MFSD2A-mediated LPC-DHA uptake across the BBB. Albumin delivers substrates such as LPC-DHA to MFSD2A expressed in brain microvascular endothelial cells. Substrate is then transported in a Na+-dependent manner across this apical membrane. How substrate is subsequently delivered across the basal membrane remains unclear (dashed lines). b, The 3.0 Å cryo-EM density map of MFSD2A_GG in complex with an Fab. Density corresponding to the N- and C-domains of MFSD2A_GG are in blue and red, respectively, and the variable region of the Fab (vFab) in green. c, The structure of MFSD2A_GG in the plane of the membrane coloured in rainbow from the N- (blue) to the C- (red) terminus. Glycosylation at two sites, and an extracellular disulphide bond are shown in stick representation, and an unresolved intracellular loop as a dashed line. d, Topology of MFSD2A showing the twelve numbered TM helices coloured as in c. Disordered regions are shown as dashed lines.
