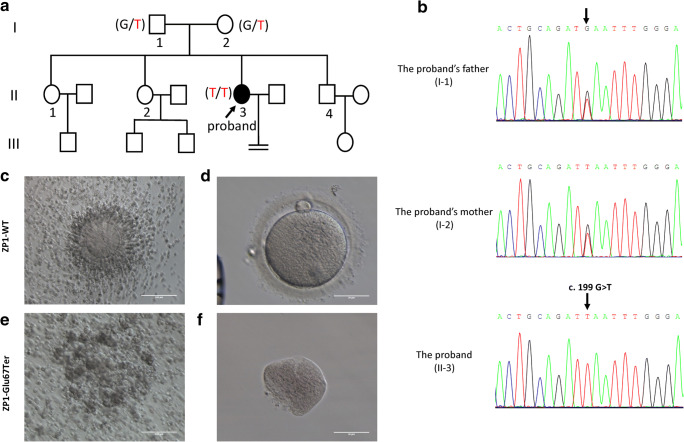
Fig. 1.
ZP1 mutation in the proband with empty follicle syndrome (EFS). a Pedigree of the patient with EFS. Male family members are denoted by squares, female family members by circles, and the EFS patient by filled circles. The arrow indicates the proband (II-3). Genotypes of the mutation c.199 G > T are noted below the symbols. b Sanger sequencing verification of ZP1 mutation, c.199 G > T. The proband carried the homozygous nonsense mutation, and the arrow shows the mutation site. Her parents harbored the heterozygous allele. c–f Analysis of oocytes morphology. c, d Normal cumulus oocyte complex and oocyte from the control undergoing intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) due to male infertility. e, f Cumulus oocyte complex and a degenerated oocyte after removing cumulus cells from the proband.