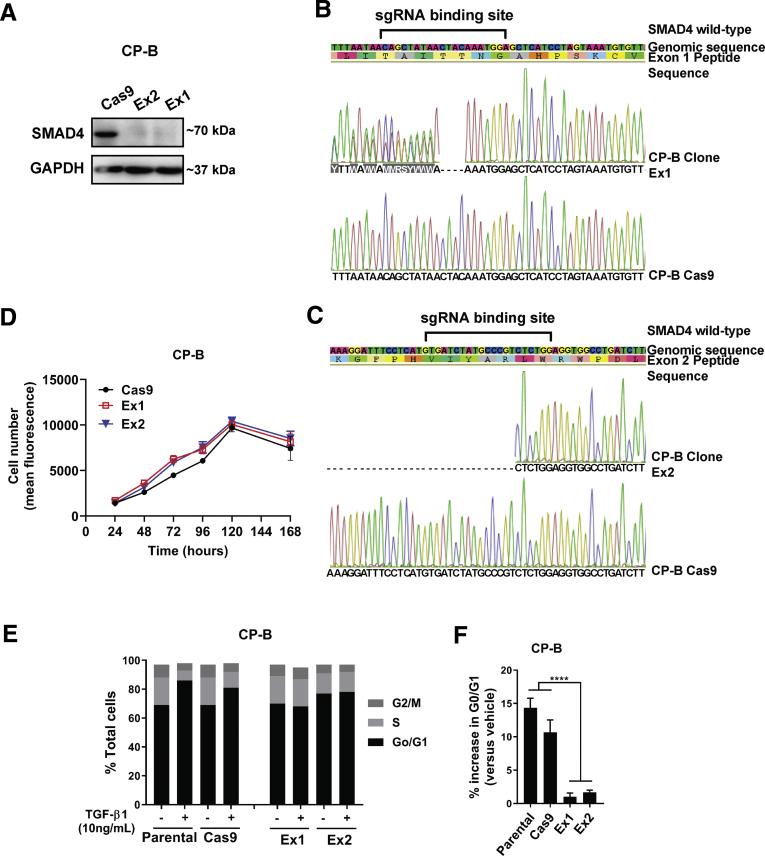
Figure 1.
SMAD4 knockout and its functional role in human esophageal high grade dysplasia CP-B cells. (A) Western blot of SMAD4 protein expression levels in CP-B SMAD4 sgRNA clonal populations Ex1 and Ex2 compared to Cas9 only control cells. Representative results from Sanger sequencing demonstrating indel mutations within (B) SMAD4 exon 1 (Ex1) and (C) exon 2 (Ex2) target sequences in 2 separate cell clones. (D) Relative cell number determined by cell viability assay (Alamar Blue) from 24-168 hours following plating of 5x103 SMAD4 knockout cells (Ex1, Ex2) or Cas9 control cells. All experiments were performed on 3 independent occasions each with 3-6 technical replicates. Data shown represent mean±SEM (N=3). (E) Representative histogram of cell cycle analyses (PI staining) in CP-B SMAD4 wild-type (Parental and Cas9) and SMAD4 knockout (Ex1 and Ex2) cells following treatment with 10 ng/mL TGF-β1 for 24 hours. (F) Percentage increase in cells arrested in G0/G1 following treatment with 10 ng/mL TGF-β1 for 24 hours. N=3 independent experiments, data represent mean ± SEM. Two-tailed Student t-test, ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.