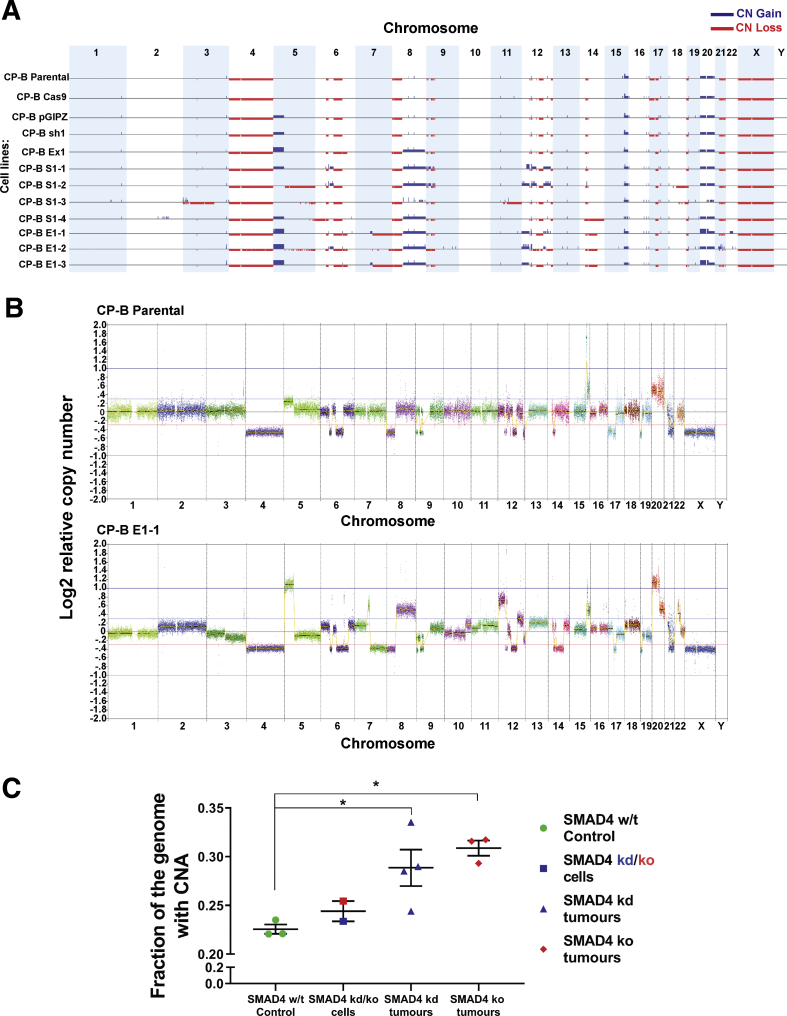
Figure 10.
Copy number alterations in CP-B cells following SMAD4 knockdown/knockout and tumorigenic transformation in vivo. (A) Genome wide copy number (CN) profile across; SMAD4 wild-type cells (CP-B Parental; CP-B Cas9; CP-B pGIPZ); SMAD4 knockout (CP-B Ex1) and SMAD4 knockdown (CP-B sh1) cells grown in vitro only; and tumorigenic SMAD4 knockdown (CP-B S1-1, S1-2, S1-3, S1-4) and knockout (CP-B E1-1, E1-2, E1-3) cells derived from xenograft tumors. See Table 1 for further details. Summary of the gains (blue) and losses (red) for individual cell lines across all chromosomes. (B) CN profile for 2 representative cell lines: CP-B Parental and CP-B E1-1. Each dot on the graph represents 50 kb normalized read count ratios. Log2 ratio equal to zero corresponds to a copy number of 2. Separate chromosomes from 1 to 22 as well as X and Y are shown and segments from highly repetitive or problematic regions were removed (see methods for details). (C) Fraction of the genome altered by CNA in cells established from SMAD4 knockdown or knockout tumor xenografts and CP-B SMAD4 wild-type controls. CP-B cells compared are SMAD4 wild-type cells, parental, pGIPZ vector only and Cas9 only (SMAD4 w/t Control), original SMAD4 knockdown or knockout (SMAD4 kd/ko cells, CP-B sh1 and CP-B Ex1) cells grown in in vitro conditions only and tumorigenic SMAD4 knockdown (SMAD4 kd tumors, CP-B S1-1 to -4) or knockout (SMAD4 ko tumors, CP-B E1-1 to -3) cells derived from xenograft tumors. Data points represent individual cell lines, bars represent mean ± SEM for each group. ∗P < .05: One way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.