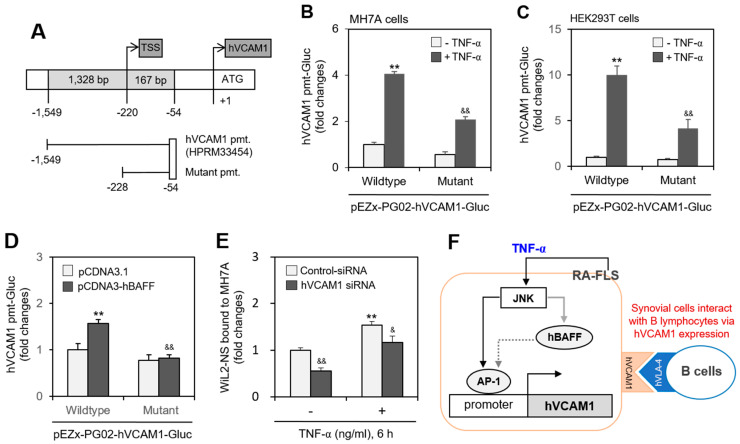
Figure 6.
WiL2-NS cell bound to MH7A cells were enhanced by human vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (hVCAM1) expression. (A–C) Mutant promoter to hVCAM1 was prepared from wild-type promoter (A). MH7A (B) or HEK293T (C) cells were transfected with wild- or mutant-type of pEZx-PG02-hVCAM gaussia luciferase (Gluc) plasmid DNA. Then, each cell was incubated for 30 h after transfection, and treated with 20 ng/mL TNF-α for additional 6 h. Gluc activity was measured by using luminometer (B,C). (D) MH7A cells were co-transfected with pCDNA3.1, or pCDNA3-hBAFF and wild or mutant type of pEZx-PG02-hVCAM-Gluc plasmid DNA by using PEI. Gluc activity was measured by using luminometer. (E) MH7A cells were transfected with control or hVCAM1-siRNA to knockdown hVCAM1 expression by using Lipofectamine® and treated with 20 ng/mL TNF-α for 6 h. Then, WiL2-NS cells were added and co-incubated to adhere for 30 min. Unbound WiL2-NS B cells were washed out and MTT assay was used to analyze bound B cells. Each experiment was performed at least four times. Data in a bar graph represent the means ± SD. ** p < 0.01; significantly different from TNF-α-untreated (B,C) or pCDNA3.1-transfected (D) or control-siRNA-treated and TNF-α-untreated (E) control group. & p < 0.05, && p < 0.01; significantly different from control TNF-α-treated (B,C) or pCDNA3-hBAFF-transfected (D) or control-siRNA-treated and TNF-α-treated (E) control group. (F) This is a schematic interaction mechanism of B lymphocytes to synovial cells by hVCAM1 expression under TNF-α stimulation. It suggests that TNF-α-activated JNK controls hVCAM1 expression via AP-1 binding on its promoter (black solid line) in synovial cells. JNK also might induce hBAFF expression (grey solid line), which lead to the regulation of hVCAM1 expression by AP-1 binding on its promoter (grey dotted line) in synovial cells. Through this molecular mechanism, hVCAM1 can control the interaction of synovial cells to B lymphocytes.