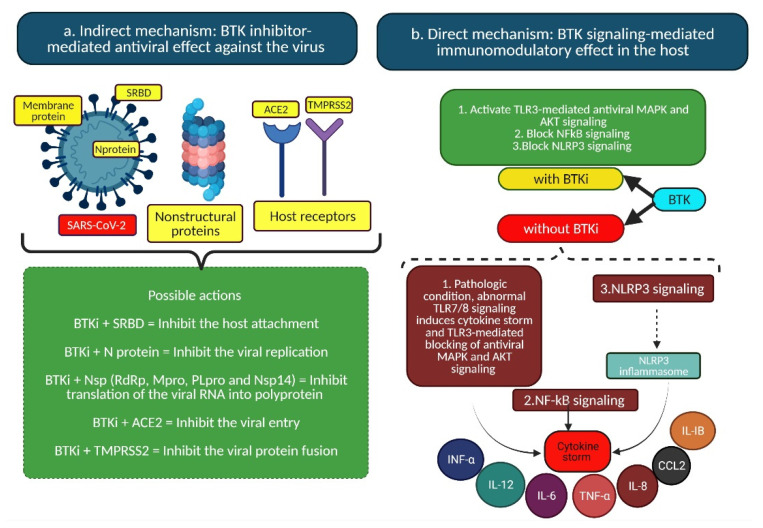
Figure 7.
Schematic illustration of the possible mechanism of action of BTK inhibitors: a) direct mechanism of BTKi with BTK signaling-mediated immunomodulatory effect in the host; b) indirect mechanism with BTKi-mediated antiviral effect against SARS-CoV-2. ACE2—angiotensin converting enzyme 2; Akt—protein kinase B; BTKi—Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor; CCL2—chemokine ligand 2; IL—interleukin; IFN—interferon; MAPK—mitogen-activated protein kinase; NSP—nonstructural protein; NF-κB—nuclear factor-κB; NLRP3—NLR family pyrin domain-containing 3; SRBD—spike protein receptor-binding domain; TLR—toll-like receptors; TMPRSS2—transmembrane serine protease 2; TNF—tumor necrosis factor.