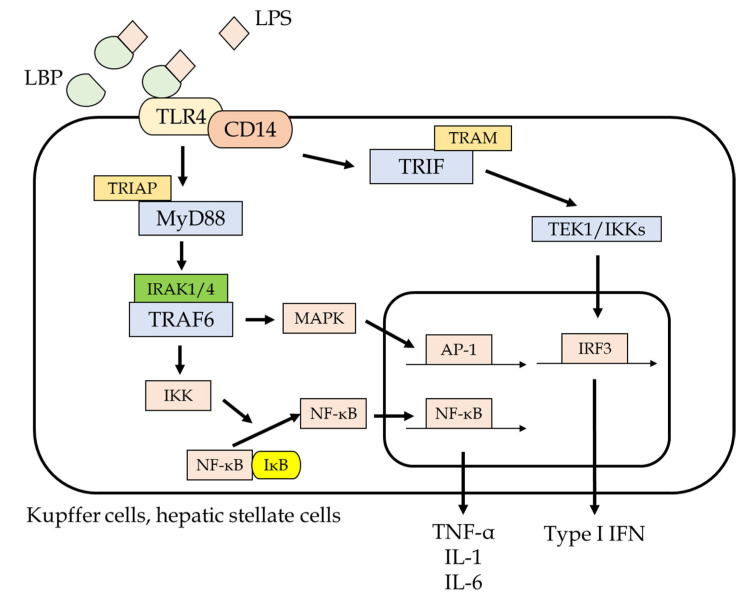
Figure 2.
Intracellular signaling of the TLR4 pathway via LPS binding. Liver cells such as Kupffer cells and hepatic stellate cells contain TLR4, which mediates the innate immunity response. LPS binding to LPS binding protein, which is a translocator for LPS, attaches to TLR4 and stimulates its downstream signal, including NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase, which induces the transcription of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines such as TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6. These inflammatory cytokines cause liver inflammation as well as activating hepatic stellate cells, leading to excessive production of the extracellular matrix, which suggests that chronic exposure of LPS can result in the progression of liver fibrosis, culminating in liver cirrhosis.