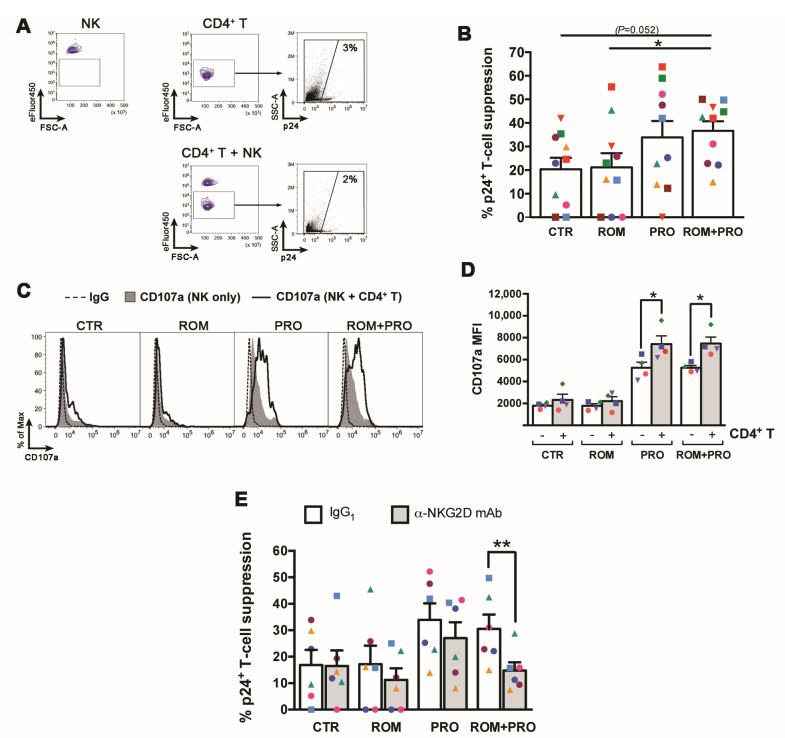
Figure 5.
Clearance of reactivated HIV+ T cells by NK cells in the presence of Prostratin and/or Romidepsin. A viral suppression assay was set up in which latently infected CD4+ T cells (targets, T) were stimulated with ROM, PRO, ROM/PRO or not stimulated (CTR) for 72 h with and without the addition in the last 18 h of autologous eFluor450-labeled, equally stimulated/not stimulated NK cells (effectors, E) at an E:T ratio of 1:1. The T and T+NK cell cultures were analysed by flow cytometry to measure the frequency of p24+ cells among gated eFluor450- targets and calculate the percentage of NK-cell mediated suppression (see Materials and Methods). (A) The gating strategy is shown for a representative set of not stimulated autologous NK cells and CD4+ T cells cultivated separately or together for the last 18 h. (B) The % of p24+ cell suppression by NK cells in CTR, ROM, PRO, and ROM/PRO co-cultures was calculated in 10 independent experiments. (C,D) NK cell degranulation was measured by including anti-CD107a mAb or IgG control to T+NK and NK cell cultures in the last 18 h; (C) CD107a expression among eFluor450+ NK cells cultivated without (filled gray) or with CD4+ T cells (open black histograms) is shown together with control IgG signal (dashed line) for a representative experiment; (D) CD107a MFI measured in 4 independent experiments is shown. (E) The suppression of p24+ cells by NK cells pre-incubated with anti-NKG2D mAb or control IgG1 was measured in 6 different donors as described in panels (A,B). Bars represent mean ± SEM. Each symbol corresponds to one donor. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 by paired t test.