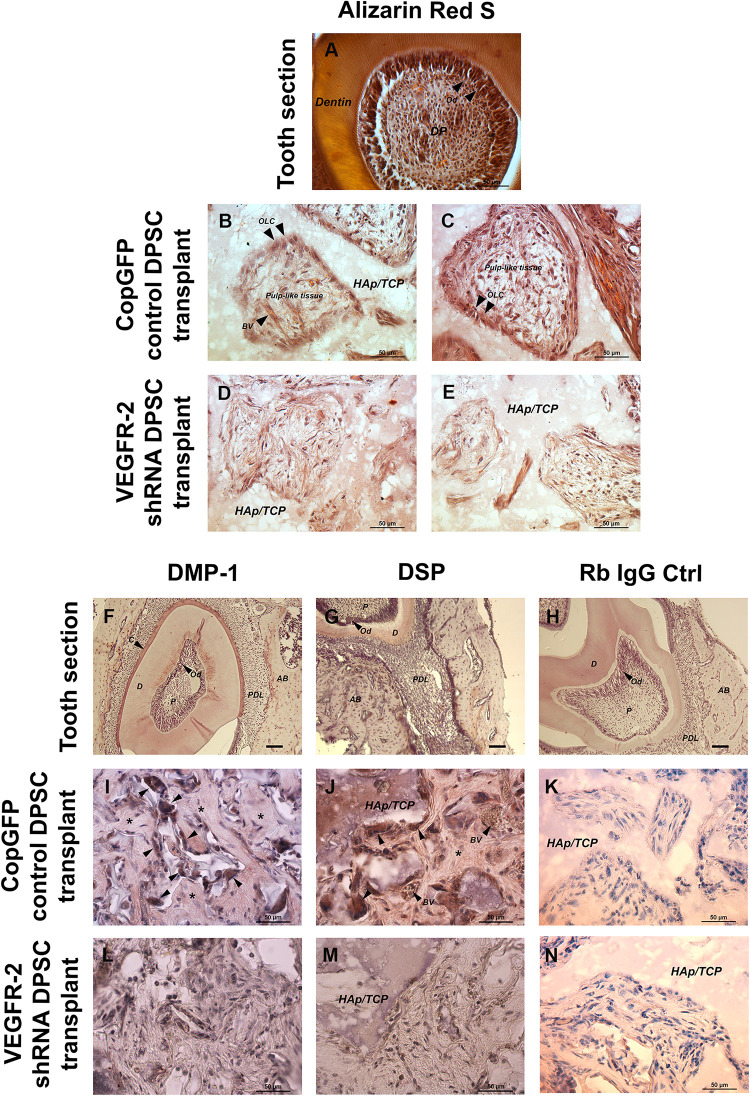
FIGURE 7.
In vivo transplantation of CopGFP control and VEGFR-2 shRNA DPSCs by Alizarin Red S staining and immunohistochemistry. Alizarin Red S staining was conducted to confirm the mineralized tissues, dental structures and morphology of CopGFP DPSC transplants and VEGFR-2 shRNA DPSC transplants. The cross-section of murine tooth was used as a positive control for Alizarin Red S staining. The positive area of Alizarin Red S showed in dentin, odontoblasts and some dental pulp regions (A). A CopGFP control DPSC transplant revealed positive staining of fibrous structure surrounding HAp/TCP with elongated and polarized odontoblast-like cells (OLC) (arrowheads). Some positive odontoblast-like cells (OLC) (arrowheads) running perpendicular to HAp/TCP and pulp-like tissues with blood capillaries were seen in CopGFP DPSC transplants (B,C). VEGFR-2 shRNA DPSC transplants only showed diffuse unpatterned cell arrangement with disorganized connective tissue (D,E). Immunohistochemistry of anti-DMP-1 and anti-DSP staining was also conducted to determine the specific dentin protein expression in the transplant tissues. The tooth sections were used as a positive control. The expression of DMP-1 and DSP was seen in dentin, cementum and alveolar bone. Both dentin matrices were very strong in the odontoblast cell layer (F,G). The CopGFP control DPSC transplants revealed the strongly positive anti-DMP-1 and anti-DSP staining in odontoblast-like cells (OCL) (arrowheads) (I,J). Its matrices were slightly stained for both markers (asterisks). The VEGFR-2 shRNA DPSC transplants showed the negative anti-DMP-1 and anti-DSP staining (L,M). The Rabbit IgG control (Rb IgG Ctrl) was used as a negative control to confirm the specificity of antibody (H,K,N). AB; alveolar bone, C; cementum, D; dentin, HAp/TCP; hydroxyapatite/tricalciumphosphate, OLC; odontoblast-like cells, P; Pulp, PDL; periodontal ligament. Scale bars indicate 50 μm.