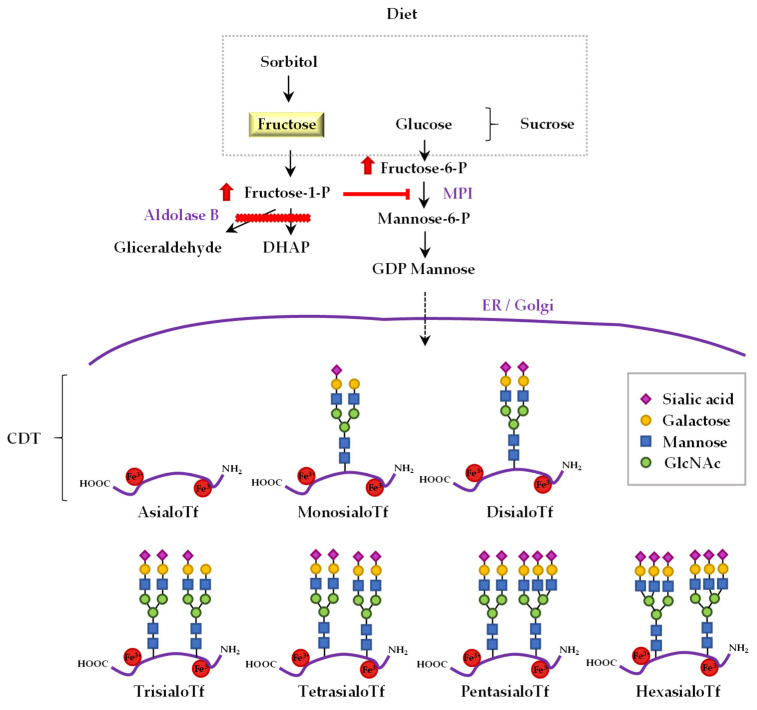
Figure 1.
The link between fructose metabolism and the profile of sialotransferrins in hereditary fructose intolerance. Dietary sorbitol and sucrose, i.e., a disaccharide formed by glucose and fructose, are precursors of fructose. The catabolic pathway of dietary fructose, sucrose and sorbitol is altered in patients with hereditary fructose intolerance (HFI). In aldolase B deficiency, the catabolism of fructose-1-P (F1P) is impaired (red bar), and this molecule is accumulated largely in the liver of HFI patients. Consequently, HFI patients have an abnormal transferrin (Tf) glycosylation pattern because of F1P-mediated competitive inhibition of mannose-6-phosphate isomerase (MPI). Tf exhibits different isoforms depending on the number of sialic acid residues present on its oligosaccharide chain; asialo-, monosialo-, disialo-, trisialo-, pentasialo-, and hexasialo-Tf. The sum of asialo-, monosialo-, and disialo-Tf is called carbohydrate-deficient Tf (CDT).