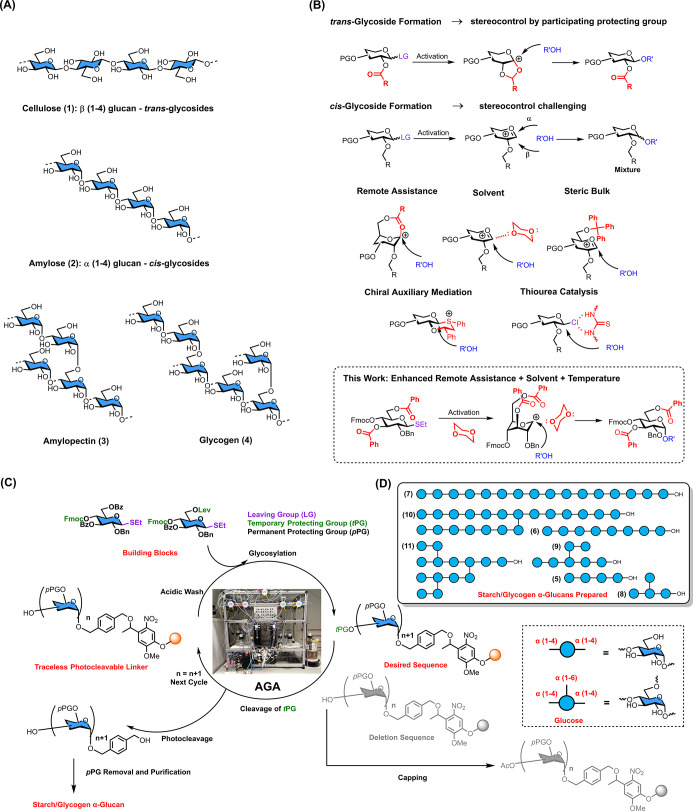
Figure 1.
Chemical structure, synthetic strategies, and Automated Glycan Assembly of starch and glycogen. (A) Chemical structure of β (1–4) linked polyglucoside cellulose (1), linear α (1–4) linked polyglucoside amylose (2), α (1–4) linked polyglucoside with α (1–6) branched α (1–4) linked polyglucoside side chains, amylopectin (3), and highly branched glycogen (4). (B) Participating neighboring protecting group ensures trans-glycoside construction, stereocontrolled cis-glycosidic bond formation is challenging: uncontrolled glycosylations result in anomeric mixtures. Typical solutions: Solvent assistance,19 bulky protecting group assistance,50 ester remote assistance,26 chiral-auxiliary-mediation,18 macrocyclic bis-thiourea catalysis.27 Strategy developed in this work for α (1–4) glucan AGA with simple chemistry. (C) Schematic view of Automated Glycan Assembly and the building blocks used to prepare cis-linked polyglucosides. (D) Synthetic amylose, and amylopectin oligo- and polysaccharides (5–11) prepared by AGA.