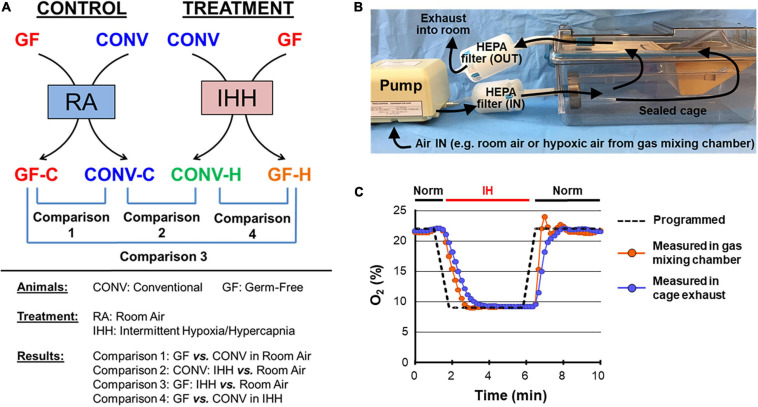
FIGURE 1.
Experiment design and instrumentation. (A) Conventional (CONV) and germ-free (GF) mice were treated with intermittent hypoxia/hypercapnia (IHH) or room air (RA) to determine the impacts of microbiome on heart transcriptome under normoxia and transcriptional response to IHH stress. (B) A tightly sealed cage system was developed to allow control of the cage atmosphere under gnotobiotic conditions by ventilating cages with a single, HEPA-filtered gas. The gnotobiotic chamber for treatment was supplied with IHH gas; room air was supplied to the control chamber. (C) A representative recording of a test run of the experimental setup with intermittent hypoxia (IH). The gas environment inside the cage was controlled by placing the pump inlet into a gas mixing chamber. IH was induced in the cage by obtaining gas from the gas mixing chamber with a programmed cycle of 5 min of 8% O2 followed by 5 min of room air (21% O2) (dashed black line). O2 levels were measured directly in the mixing chamber (red symbols) or in the exhaust gas of the ventilated cage (blue symbols). IH, intermittent hypoxia; Norm, normoxia.