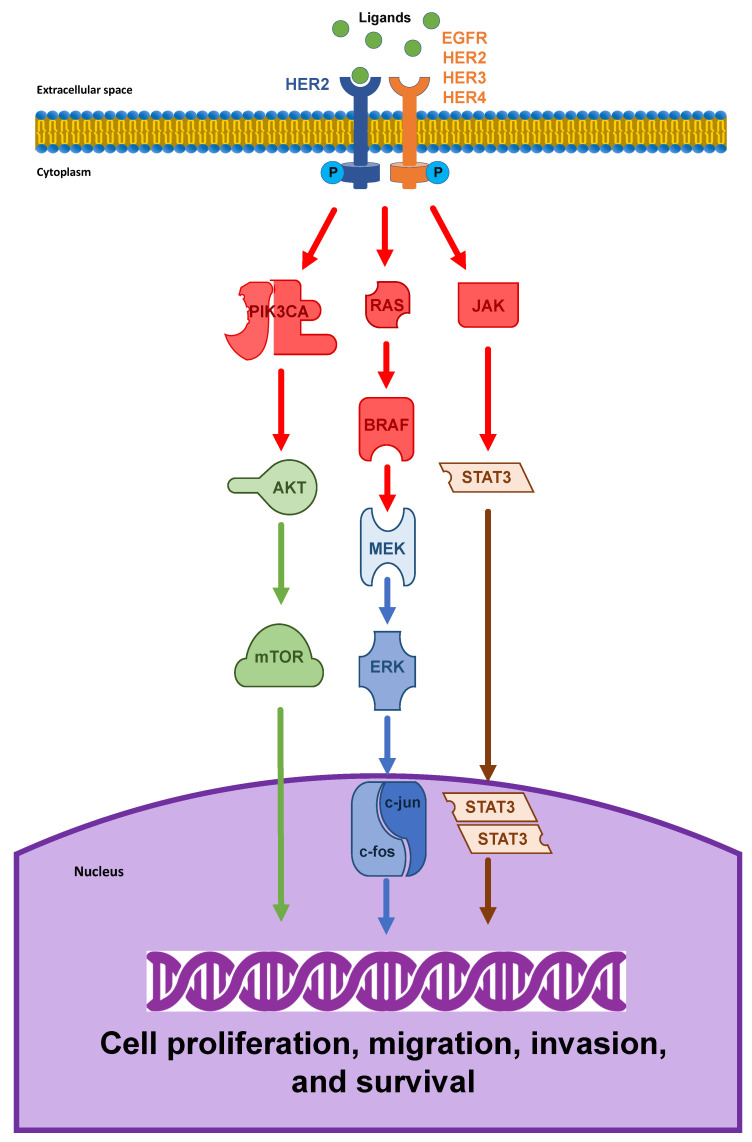
Figure 1.
The HER2 pathway in tumorigenesis. Ligand binding to the extracellular domain of human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER2) stabilizes the dimerization between HER2 and another member of EGFR family receptors (EGFR, HER2, HER3, and HER4). By transphosphorylation of tyrosine residues within the cytoplasmic domains, the active homodimers or heterodimers thereafter stimulate several signaling cascades, such as the PI3K/AKT, the RAS/MAPK, and JAK/STAT pathways. These downstream pathways result in the transcription of genes driving tumor cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and survival.