FIGURE 4.
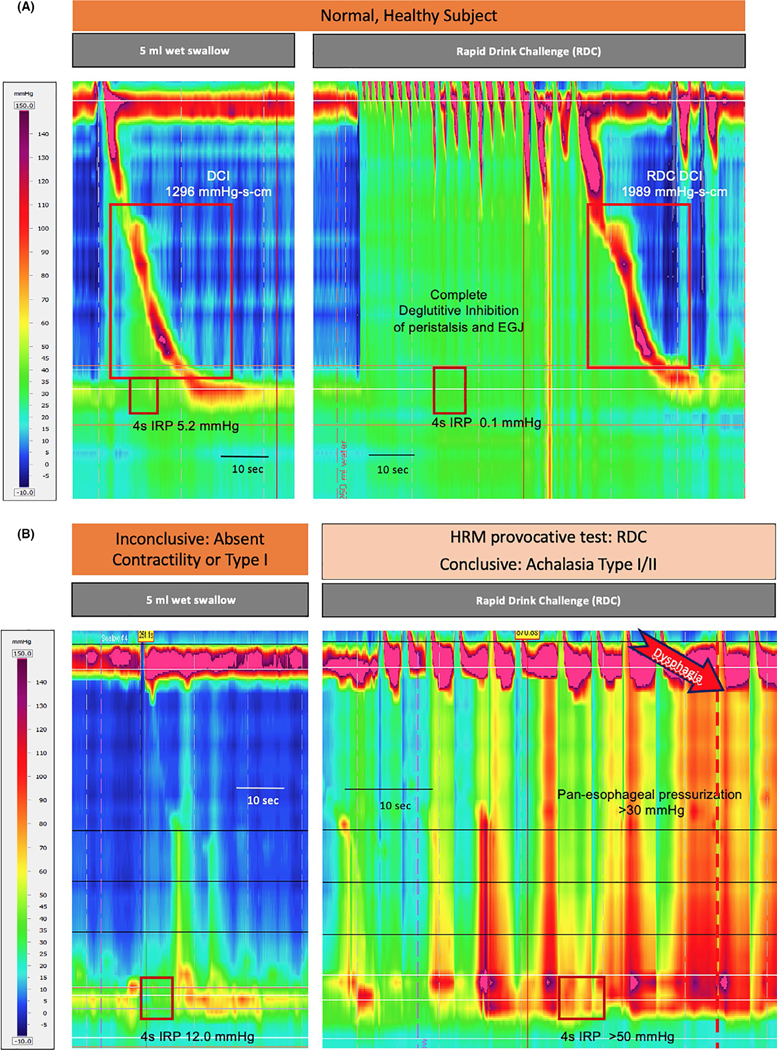
Rapid Drink Challenge (RDC) is performed by asking the subject to drink a large volume of water (100–200 ml) by a series of swallows. The rate can be controlled by drinking through a straw. In healthy subjects, similar to MRS, RDC highlights deglutitive inhibition during repeated swallows (upper panel). Additionally, the presence of a normal contraction sequence following the RDC is a specific marker of normal contractility; however, this is not observed in all healthy controls. Rapid Drink Challenge (RDC) highlights failure of deglutitive inhibition in patients with achalasia (lower panel). In this case the patient had inconclusive findings with normal IRP during wet swallows (left panel). RDC revealed conclusive evidence of achalasia with pan-esophageal pressurization and IRP >50 mm Hg. The patient responded to pneumatic dilatation. Images courtesy of Functional GI Laboratory, Zürich University Hospital.
