Table 2.
Characteristics and summary, of studies included for research question 3.
| (a) Obesity in Women and Gut Microbiome | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Sample Size | Patient Characteristics | Gut Microbiota Analysis | Main Findings |
| Menni et al. (2016) |
n = 544 women with weight loss: BMI from 25.4 to 24.4 (group 1) n = 544 women with little weight gain: BMI from 24 to 25.2 (group 2) n = 544 women with heavy weight gain BMI from 25.4 to 28.8 (group 3) |
Group 1 Age (yrs) 49.91 ± 9.49 Group 2 Age (yrs) 50.11 ± 5.54 Group 3 Age (yrs) 49.25 ± 8.48 All groups 15% smokers, further no exclusions. |
V4 region of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene was amplified and sequenced on Illumina. De novo OTU clustering was carried across all reads using Sumaclust within QIIME 1.9.0. Alpha diversities → Shannon index, OTU counts. |
Alpha diversity (Shannon index): Group 1 (weight loss) 5.21 Group 2 (weight gain) 5.19 Group 3 (heavy weight gain) 5.07 (p < 0.05) Alpha diversity (OTU): Group 1 346.3 Group 2 348 Group 3 331.8 (p < 0.05) Family Bacteriodes
|
| Chavez-Carbajal et al. (2019) |
n = 25 control women n = 17 obese women n = 25 obese women with metabolic syndrome |
Controls Age (yrs) 23.3 ± 3.1 BMI (kg/m2) 21.4 ± 1.9 Obesity Age (yrs) 28.8 ± 8.4 BMI (kg/m2) 34.8 ± 6.1 Obesity + metabolic syndrome (ms) Age (yrs) 40.5 ±10.3 BMI (kg/m2) 35.8 ± 5.1 Only women to avoid gender bias Controls significant different in age and bmi from other 2 groups |
V3 region of the 16S rDNA Amplicon PCR amplification using PCR GeneAmp System 2700 Thermal Cycler. Determine with an open reference the OTUs and using a 97% similarity using QIIME pipeline (v1.9.0) and Geengenes database v13.8. Alpha diversity → Observed Species, Chao1, Shannon, Simpson. |
Alpha diversity (Shannon index) Controls 4.9 Obesity 5.23 Obesity + MS 5.15 Dominant phyla in all groups: Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria Phyla Frimicutes
Obesity and obesity + MS
Faecalibacterium (phyla firmicutes) Controls 0.55%
Controls 0.89%
Controls 0.99%
Controls 2.18%
Controls 1.74%
|
| Miranda er al. (2017) Observational study |
n = 31 controls n = 32 normal BMI but high body fat percentage. n = 33 obesity |
Controls Age (yrs) 16.3 ± 0.8 Gynoid fat (%) 34.5 (30.6–36.7) High body fat Age (yrs) 16.5 ± 0.9 Gynoid fat (%) 39.7 (37.9–46.9) Obesity Age (yrs) 16.2 ±1.3 Gynoid fat (%) 48.0 (45.5–54.1) |
RT-qPCR to analyze microbiota CFX96 Touch™ detection system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) Alfa diversity → Shannon index |
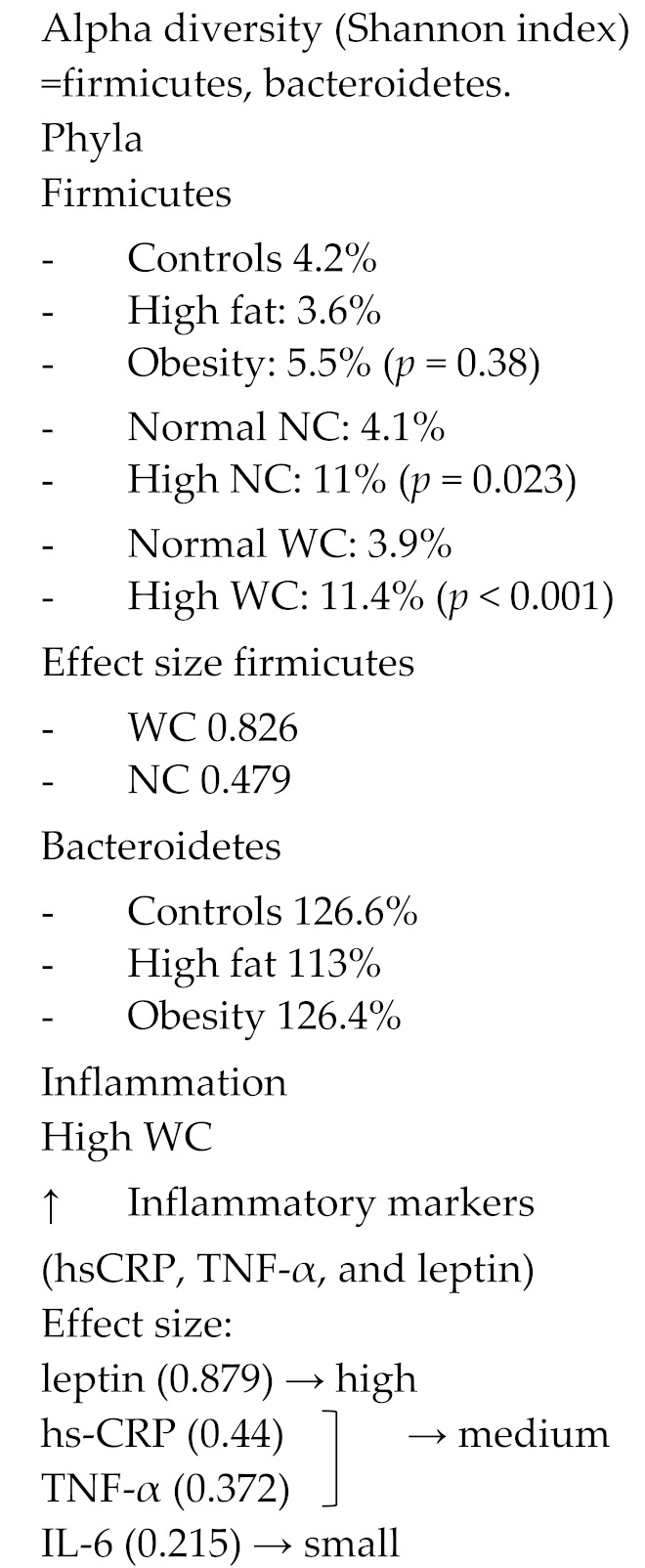
|
| Pekkala et al. (2015) |
n = 4 women with high TLR gene expression (BMI 31) n = 4 women with low TLR gene expression (BMI 28) |
High TLR gene expression Age (yrs) 35.5 ± 6.0 BMI (kg/m2) 31 ± 2.0 Low TLR gene expression Age (yrs) 56.9 ± 6.4 BMI (kg/m2) 28 ± 2.5 BMI significantly higher in High TLR group. |
Real-time PCR analysis was performed using in-house designed primers, iQ SYBR Supermix and CFX96 TM Real-time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad Laboratories) Real-time PCR analysis was performed using in-house designed primers, iQ SYBR Supermix and CFX96 TM Real-time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad Laboratories) Real-time PCR analysis was performed using in-house designed primers, iQ SYBR Supermix and CFX96 TM Real-time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad Laboratories) RNA extraction and rt-PCR analysis using in-house designed primers. |
Alpha diversity High TLR group: significant dysbiosis. Phyla Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio
|
| Ott et al. (2018) |
n = 20 women (own controls) n = 20 after diet n = 20 14 days after diet |
Women Age (yrs) 46.8 ± 11.5 Before diet BMI (kg/m2) 34.9 ± 3.8 After diet BMI (kg/m2) 32.5 ± 3.5 14 dys after diet BMI (kg/m2) 32.6 ± 3.8 |
16 S rRNA gene amplicons were sequenced in paired-end modus (PE275) using a MiSeq system (Illumina) | Alpha diversity No differences Phyla Protobacteria
|
| Choi et al. (2017) Animal study |
n = 3 SHAM mice n = 3 SHAM-HF n = 5 ovariectomized mice (OVX) n = 5 OVX-HF |
SHAM Weight (g) 29.96 ± 2.13 LDL (mg/dL) 30.9 ± 5.1 SHAM-HF Weight (g) 53.13 ± 3.88 LDL (mg/dL) 78 ± 4.4 OVX Weight (g) 41.44 ± 1.52 LDL (mg/dL) 45.1 ± 9.1 OVX-HF Weight (g) 57.54 ± 3.84 LDL (mg/dL) 95.7 ± 12.3 Weight significantly different |
V3-V4 16S rRNA amplification following the 16S Metagenomic Sequencing Library Preparation guide by Illumina. Gene-enrichment and functional annotation analysis performed using gene ontology and KEGG pathway analysis. |
Alpha diversity (Shannon index)
Firmicutes
SHAM
Akkermansia muciniphila related to
|
| (b) Obesity and Gut Microbiome: Sex Differences | ||||
| Study | Sample Size | Patient Characteristics | Gut Microbiota Analysis | Main Findings |
| Haro et al. (2016) |
n = 39 men n = 13 men < BMI 30 n = 13 BMI 30–33 n = 13 men BMI > 33 n = 36 women n = 13 BMI < 30 n = 10 BMI 30–33 n = 23 BMI > 33 |
Men BMI < 30 Age (yrs) 63.2 ± 2.0 BMI (kg/m2) 27.6 ± 0.6 LDL (mg/dL) 76.6 ± 4.2 BMI 30–33 Age (yrs) 58.9 ± 2.4 BMI (kg/m2) 31.4 ± 0.3 LDL (mg/dL) 95.3 ± 6.0 BMI > 33 Age (yrs) 61.3 ± 2.2 BMI (kg/m2) 35.3 ± 0.7 LDL (mg/dL) 87.8 ± 2.1 Women BMI < 30 Age (yrs) 60.1 ± 2.6 BMI (kg/m2) 27.0 ± 0.8 LDL (mg/dL) 94.2 ± 9.4 BMI 30–33 Age (yrs) 62.4 ±2.3 BMI (kg/m2) 31.4 ± 0.3 LDL (mg/dL) 87.1 ± 7.6 BMI > 33 Age (yrs) 58.9 ± 2.3 BMI (kg/m2) 36.7 ± 1.4 LDL (mg/dL) 80.4 ± 4.4 |
Sequencing V4 16S microbial rRNA on the Illumina MiSeq. Taxonomy assigned to OTUs against the Greengenes v13-8 preclustered at 97% identity. Alpha diversities → observed OTU counts, Shannon, Simpson. |
Alpha diversity similar men and women and comparing BMI Phyla Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio
Women BMI > 33
Women BMI > 33
|
| Min et al. (2019) |
n = 116 women n = 96 men |
Women Age (yrs) 50.7 ± 14.1 BMI (kg/m2) 23.0 ± 3.0 Gynoid fat 15.9 ± 3.0 Android fat 12.5 ± 1.2 LDL (mmol/L) 2.7 ± 0.7 Men Age (yrs) 50.7 ± 14.5 BMI (kg/m2) 23.6 ± 3.0 Gynoid fat 17.7 ± 3.0 (p < 0.005) Android fat 9.9 ± 1.4 (p < 0.005) LDL (mmol/L) 2.8 ± 0.7 |
16S rRNA V4 region sequencing The denoised sequences are mapped to the GreenGenes reference database43. Taxonomy is assigned at 97% identity. Alfa diversity → Shannon index |
Alpha diversity potential negative association between gynoid fat ratio and microbiome abundance in both sexes. In women compared to men different taxa responsible for relation between fat distribution and diversity. Gynoid fat ratio positive correlation Women:
|
