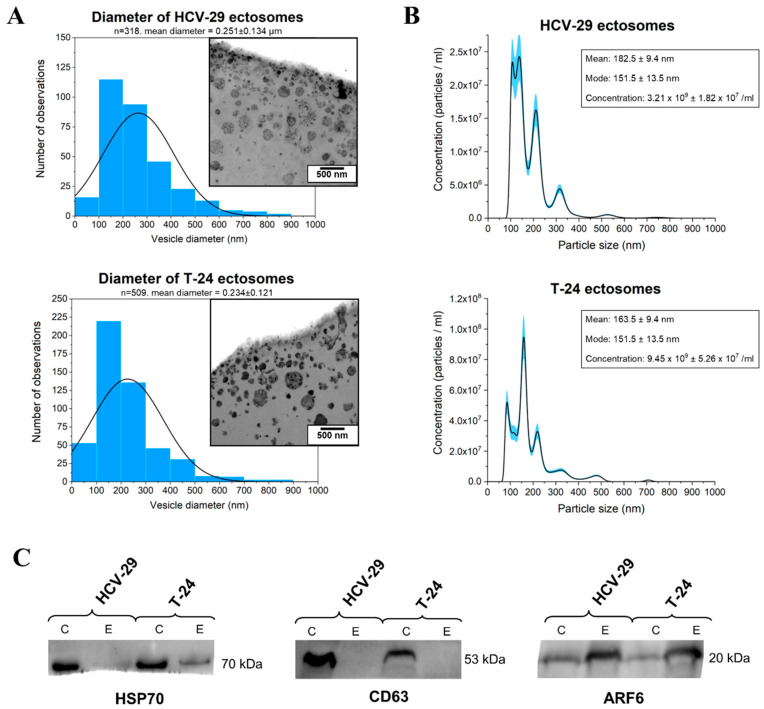
Figure 1.
Characterization of ectosome samples isolated from conditioned media of T-24 urothelial bladder carcinoma and HCV-29 normal ureter epithelial cells. (A) Morphological characterization of HCV-29- and T-24-derived ectosomes by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Size distributions are presented on histograms. Mean diameter ± standard deviation was calculated for all observed vesicles (n) from a given sample. (B) Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) of HCV-29- and T-24-derived ectosomes. Results from five independent measurements for each cell line are presented on graphs. The shaded area depicts standard deviation. (C) Representative Western blot of extracellular vesicle markers in whole-cell protein extracts (lines C) and ectosome samples (lines E). Fifty μg of proteins separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and transferred into PVDF membrane were probed with anti-HSP70 (1:2000), anti-CD63 (1:2000) and anti-ARF6 (1:500) as primary antibodies and anti-mouse IgG-HRP (1:400) as a secondary antibody.