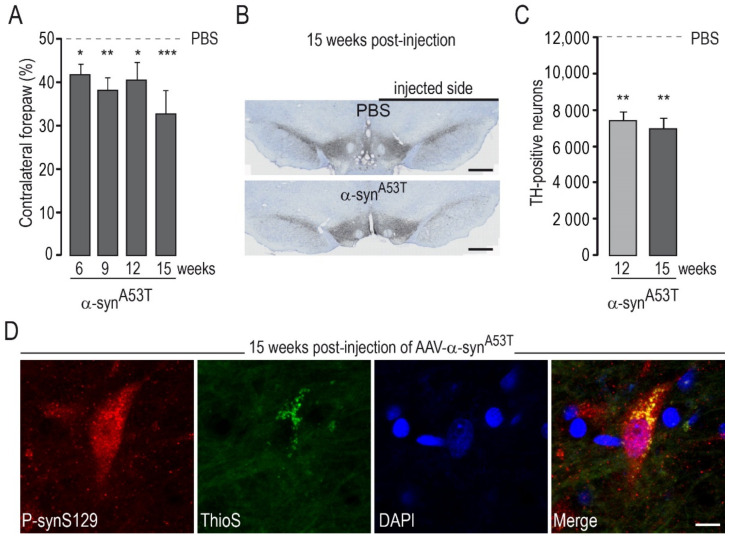
Figure 2.
Degeneration and motor symptoms produced by intra-nigral injection of AAVs encoding α-synA53T. AAV-α-synA53T (2.5 × 1010 Vg) or vehicle (PBS) were unilaterally injected into the rat SNpc. The cylinder test, which assesses asymmetry of forepaw use, was performed at various timepoints (6–15 weeks) post-injection (PI). Two subgroups of rats were processed for histological evaluation (ICH) at 12 and 15 weeks PI. (A) Results of the cylinder test at various time points after AAV injection. (B) Representative photomicrographs of the SNc in rats injected with AAV-α-synA53T or vehicle (PBS) labeled by Tyrosine Hydroxylase (TH) immunohistochemistry. (C) Number of TH-positive neurons in the SNpc measured using unbiased stereology showing a consistent decrease in the number of TH-positive neurons. (D) Representative confocal images obtained by double immunofluorescence analysis in the SNpc of rats injected with AAV-α-synA53T at 15 weeks PI: neurons with α-syn phosphorylated at serine 129 (p-synS129) (in red). The neuron with high levels p-synS19 immunoreactivity is also positive for ThioS (in green), suggesting that p-synS129 accumulation corresponds, at least partially, to aggregated forms of α-syn. Results are expressed as the means ± the SEM. N = 8–12 animals/group. ANOVA and PLSD post hoc test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001. Scale bars: B, 750 µm; D, 10 µm.