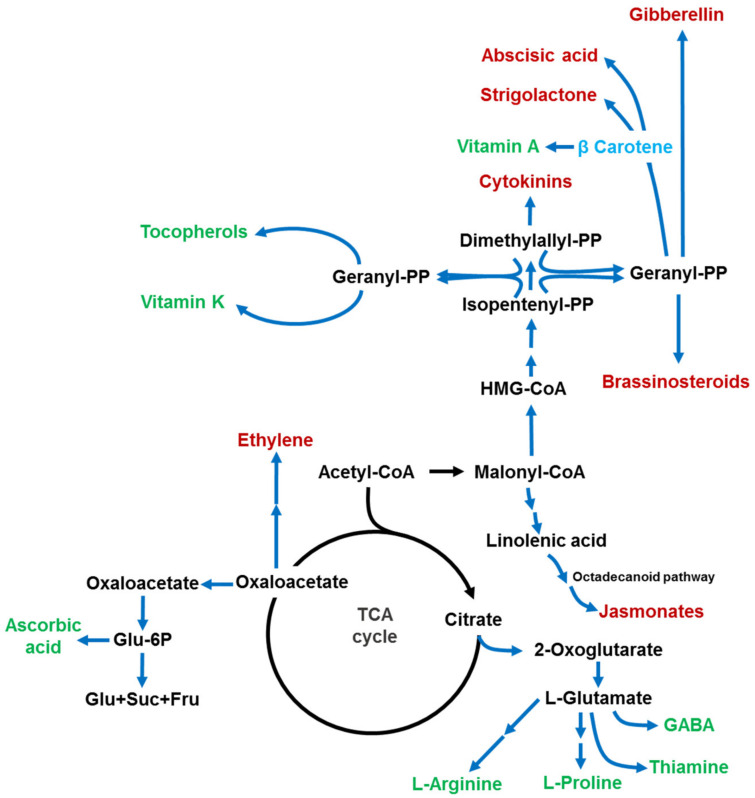
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of CA metabolism in plants. Citrate derived from the TCA cycle can be converted to acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase converts acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA, a precursor for fatty acid and jasmonate biosynthesis via the octadecanoid metabolic pathway. Malonyl Co-A also feeds into the mevalonate pathway and provides building blocks of phytohormones (cytokinins, gibberellins, abscisic acid, brassinosteroids, and strigolactones) and vitamins (vitamin K and vitamin A). Oxaloacetate (OAA) can be converted into glucose-6-phosphate via PEP caroxykinase and phosphatases, providing a source of ascorbic acid as well as glucose, sucrose and fructose. 2-oxoglutarate can be converted into glutamate, feeding into GABA and amino acid biosynthesis.