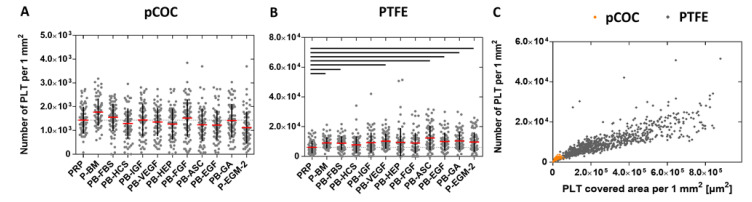
Figure 4.
Polymer-dependent promotion of platelet (PLT) adherence. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) was incubated under static conditions for 1 h at 37 °C with basal medium (BM) or with BM containing one of nine different supplements or with BM containing all nine supplements (see Table 1 for nomenclature) in a ratio of 1:1 resulting in a concentration of 50,000 PLT µL−1. PRP served as control. Images of phalloidin-stained PLT were quantitatively analyzed by ImageJ software. Shown are the number of adherent PLT on COC (A) and PTFE (B) as well as the relationship between PLT number and PLT covered area (C). Thin dashed line shows the value for PRP (control). Data represent the arithmetic mean (red) ± standard deviation (black), n = 72 per supplement. Black lines indicate significant differences with p ≤ 0.0475. A comparison of the two substrates regarding thrombogenicity shows that PTFE (grey rhombuses) is more thrombogenic than COC (orange circles; C). n = 864 for each polymer.