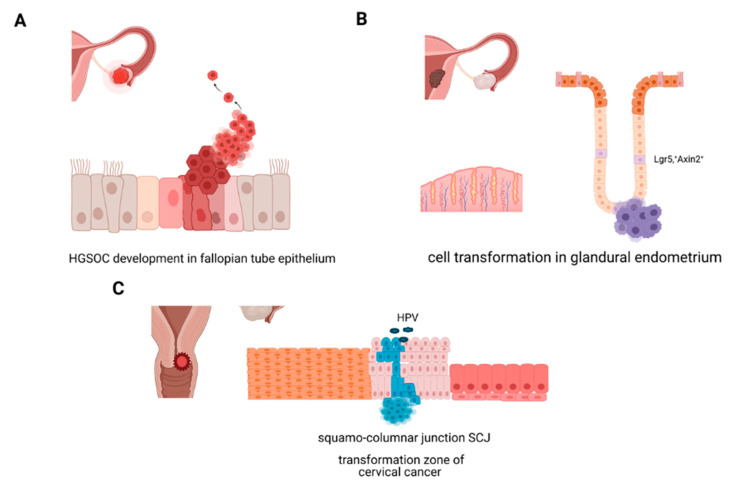
Figure 1.
Overview of cell transformation mechanism in ovarian, uterine and cervical cancers. (A) HGSOC develops from secretory cells of fallopian tube epithelium. (B) Model of endometrial cancer development postulates central role of the stem cells in the uterine glands during the transformation. (C) Cervical cancer arises in the transformation zone/squamo-columnar junction of the cervix and is driven by HPV viral infection.