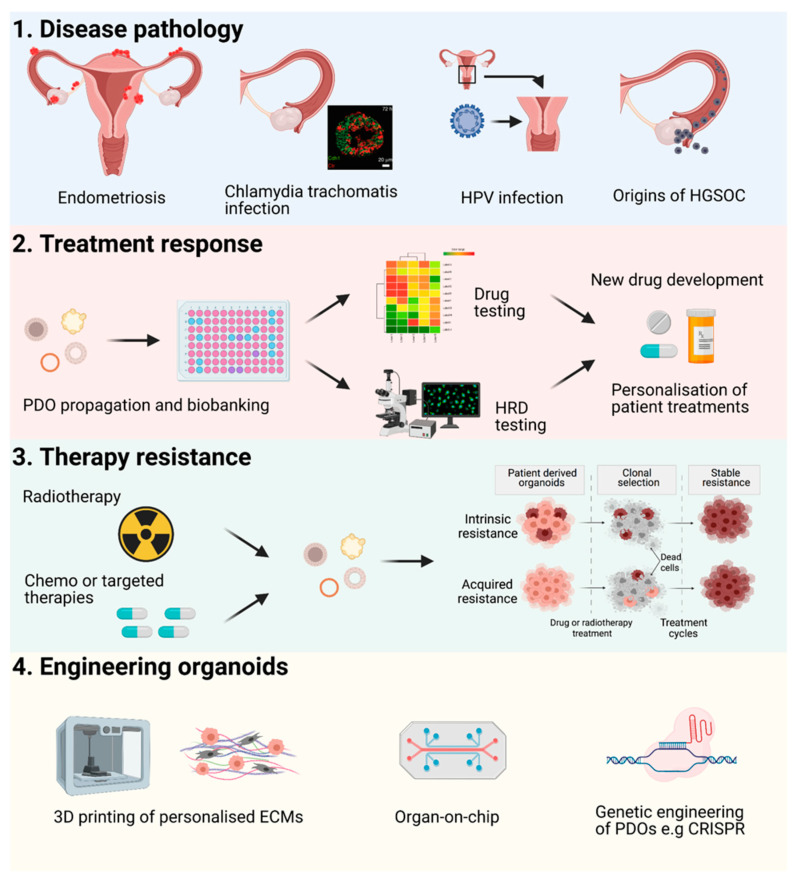
Figure 2.
Overview of the applications of organoids in the research of gynaecological malignancies. 1. Organoids can model different cell processes and disease pathology such as endometriosis, bacterial infections such as Chlamydia trachomatis, HPV infection leading to cervical cancer, and investigating the origins of HGSOC. 2. PDOs can also be propagated for long-term biobanking for future regeneration. PDOs are amenable to drug screening to mimic patient drug responses to guide personalisation of therapy or improve pharmaceutical drug discovery rates. Assays to assess homologous recombination capacities of PDOs can also be performed. 3. PDOs can also be used to model cancer progression and development of resistance to standard-of-care patient therapies. 4. Future applications for engineering of organoids to improve derivation rates include 3D printing of tailored extra-cellular matrices, introducing fluid flow with microfluidics or organ-on-chip technologies. PDOs can also be genetically engineered for example via CRISPR technology to mimic disease genomes.