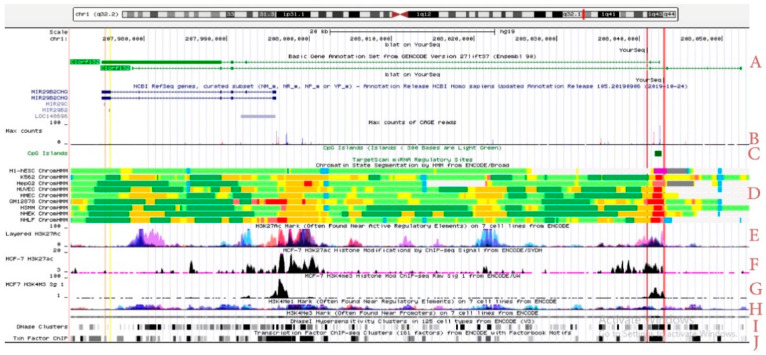
Figure 2.
The genomic features of miR29b2c precursor. To make it easier to follow, the location of miR-29b2 and miR-29c are highlighted with yellow and purple color bands, respectively, and the potential distal transcription start sites of MIR29B2CHG with red color bands. As it is evident in the figure, there are several spliced variants for the miR29b2c precursor. In addition to the miR29b2c precursor (short variants), there are also longer variants of C1orf132 (A). Other bioinformatics features (UCSC Genome Browser hg19) support the existence of other start sites for C1orf132 transcription, including: Max counts of CAGE reads belonging to FANTOM5 summary (B), CpG island (C), active promoter-predicted elements according to Broad ChromHMM (D), active or potentially active regulatory elements of layered and MCF7 cells H3K27ac mark (E,F), active or potentially active promoter and enhancer regions marks by H3K4me3 and H3K4me1, respectively (G,H), DNase cluster (I), and transcription factor ChIP (J).