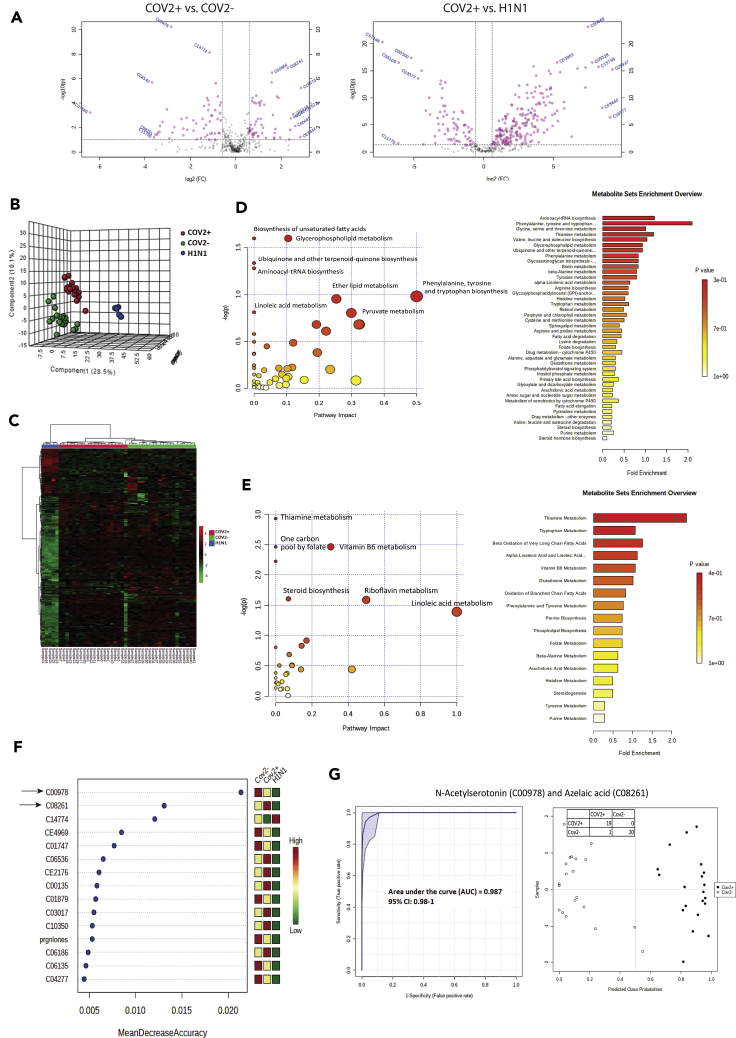
Figure 2.
Metabolic phenotype of the respiratory specimen is predictive of SARS-CoV2 infection
(A) Volcano plot showing differentially expressed metabolites in COVID-19-positive vs. COVID-19-negative respiratory specimen and COVID-19-positive vs. Influenza A H1N1 pdm 2009-positive (Pink dots are significant [p < 0.05, FC > 1.5]).
(B) Partial least square discriminant analysis showing clear segregation of COVID-19-positive patients (Red dots) from COVID-19-negative (Green dots) and influenza A H1N1 pdm 2009-positive cases patients (Blue dots) based on metabolomic estimations.
(C) Hierarchical cluster (Heatmap) analysis of the metabolites identified in the study (p < 0.05) show clear segregation of COVID-19-positive patients (Red bar) from COVID-19-negative (Green bar) or Influenza A H1N1 pdm 2009-positive cases patients (Blue bar; Red = upregulated, Green = downregulated and black = unregulated).
(D) Random forest analysis showing the mean decrease in accuracy of the metabolites (Red = upregulated and Green = downregulated and yellow = unchanged) in COVID-19-positive as compared to COVID-19-negative or influenza A H1N1 pdm 2009-positive patients.
(E) Joint AUROC analysis of N-acetylserotonin (C00978) and azelaic acid (C08261) and documenting an AUC = 0.987 CI (0.98–1) p < 0.05 along with prediction class probability score plot showing segregation of CoV2 positive and CoV2 negative.
(F) Pathway and metabolite set enrichment analysis (KEGG) for the upregulated metabolites (FC > 1.5, p < 0.05) in COVID-19-positive respiratory specimen as compared to COVID-19-negative or influenza A H1N1 pdm 2009-positive specimen.
(G) Pathway and metabolite set enrichment analysis (KEGG) for the downregulated metabolites (FC > 1.5, p < 0.05) in COVID-19-positive respiratory specimen as compared to COVID-19-negative or Influenza A H1N1 pdm 2009-positive specimen.