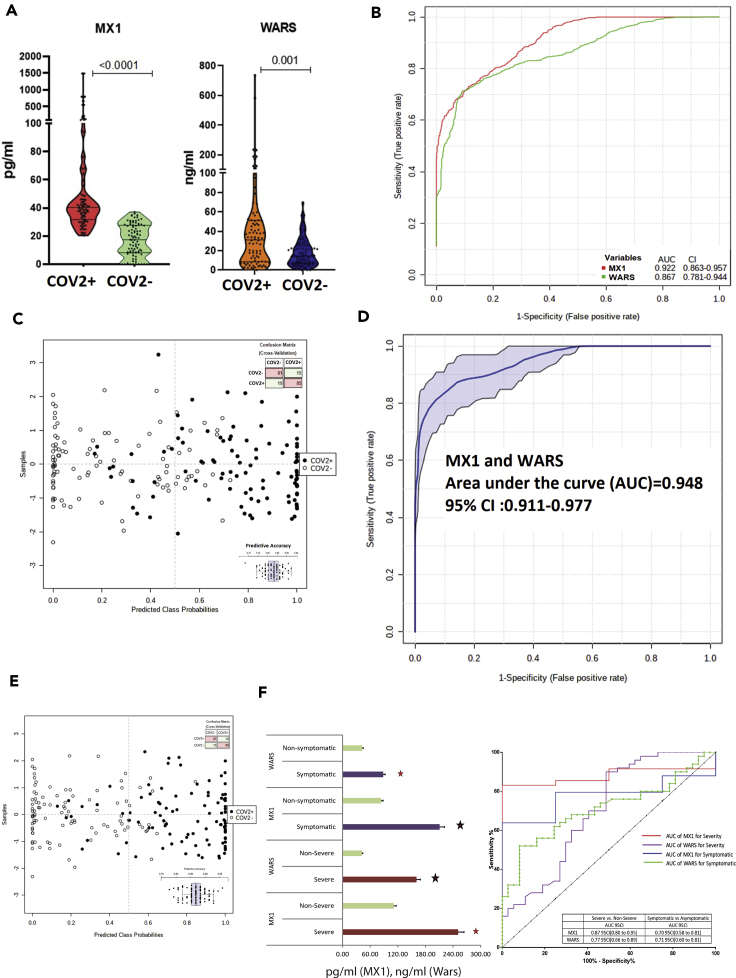
Figure 4.
Estimation of MX1 and WARS as candidate indicators for SARS-CoV-2 infection and outcome
(A) Quantitative assessment of MX1 and WARS in the respiratory specimen of 200 COVID-19 specimen show significant increase in MX1 and WARS levels in COVID-19 positive as compared to COVID-19 negative (FC > 2, p < 0.05)
.(B) Multivariate area under the receiver operating curve analysis show significant AUC of MX1 = 0.922 CI (0.863–0.957) and WARS = 0.867 CI (0.781–0.944).
(C) Prediction class probability for MX1 alone show clear segregation of COVID-19-positive from COVID-19-negative patients with a predictive accuracy of 84%.
(D) Area under the receiver operating curve analysis for MX1 and WARS together show AUC = 0.948 CI (0.911–0.977) p < 0.05.
(E) Prediction class probability for MX1 and WARS together show clear segregation of COVID-19-positive from COVID-19-negative patients with a predictive accuracy of 86%.
(F) Quantitative assessment of MX1 and WARS in the respiratory specimen show significant increase in MX1 and WARS levels in severe COVID-19 (n = 10) as compared to non-severe COVID-19 (n = 90, FC > 2, p < 0.05). The right panel show multivariate area under the receiver operating curve analysis of MX1 and WARS for the assessment of severity and symptomatic patients in COVID-19.