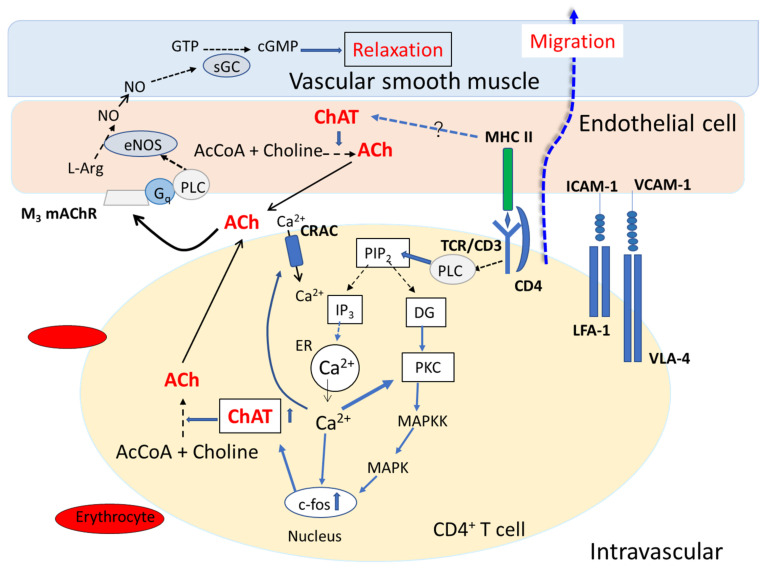
Figure 2.
Schematic drawing illustrating the interaction between a vascular endothelial cell (VEC) and a CD4+ T cell, leading to cholinergic activation and transendothelial migration of the T cell. Interaction between vascular endothelial cells (VECs) and CD4+ T cells is mediated by specific interactions between major histocompatibility complex II (MHC II) and the T cell receptor/CD3 complex (TCR/CD3), between intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1), and between vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and very late antigen-4 (VLA-4). Stimulation of TCR/CD3 signaling pathways in CD4+ T cells activates phospholipase C (PLC), leading to conversion of phosphatidyl 4,5-bisphospahe to inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DG). IP3 induces Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The released Ca2+ induces influx of extracellular Ca2+ through the calcium release-activated channel (CRAC). DG with Ca2+ activates protein kinase C (PKC). PKC activates mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase (MAPKK), which in turn activates MAPK. MAPK promotes c-fos mRNA expression in the nucleus, leading to up-regulation of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) mRNA expression (see reviews by [23,28]). Little is known about the regulatory mechanisms governing ACh synthesis and release in VECs. However, given that MAPK activation and c-Fos protein levels are closely connected in MHC-II signaling [29], one could speculate that TCR-induced transmembrane signaling elicited by MHC II enhances ChAT mRNA expression in VECs. ACh synthesized from choline and acetyl coenzyme A (AcCoA) in a reaction catalyzed by ChAT in both VECs and CD4+ T cells is released and acts on M3 mAChRs expressed on the surface of VECs. The M3 mAChR activation leads to nitric oxide synthase (NOS)-catalyzed production of NO from L-arginine (L-Arg). NO activates soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC), which catalyzes the production of cGMP and relaxes the vascular smooth muscle. Relaxation of vascular smooth muscle facilitates the extravasation of CD4+ T cells.