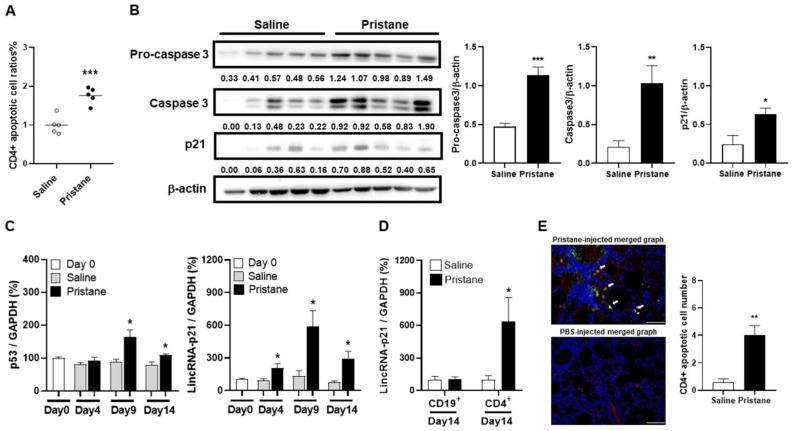
Figure 4.
Induction of CD4+ cell apoptosis and apoptosis-related molecules with increased lincRNA-p21 expression in pristane-injected mice. (A) CD4+ apoptotic cell ratios on day 14 from PBS- and pristane-injected mice. (B) Representative immunoblot assay with quantitation of signal intensity for procaspase 3, caspase 3 and p21 expression in CD4+ splenocytes from PBS- and pristane-injected mice. (C) Serial p53 (left panel) and lincRNA-p21 (right panel) splenic expression levels on day 0, 4, 9 and 14 from PBS- and pristane-injected mice. (D) LincRNA-p21 expression levels in splenic CD4+ and CD19+ cells on day 14 from PBS- and pristane-injected mice. (E) Representative IF staining of TUNEL (green) and CD4 (red) in lung tissues on day 14 from PBS- and pristane-injected mice (left panel, ×400). Cell nuclei counterstained with DAPI (blue). Arrows indicating CD4 and TUNEL double-positive cells in the merged photograph. Bars shown on photomicrographs corresponding to 20 µm. CD4+ apoptotic cell numbers in lung tissues on day 14 from PBS- and pristane-injected mice, as determined by averaging the number from 3 fields (×400) of the highest density of positively stained cells in each section (right panel). Relative abundance of a measured gene expression was normalized by GAPDH gene from each sample. The average levels of mouse splenocytes on day 0 and purified cell subpopulations of PBS-injected mice on day 14 were determined as 100%. Five mice per group in (A–E) experiments. Values are mean ± SEM. All of the in-vivo and ex-vivo results in Figure 4 were representative of two independent experiments with similar findings. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.