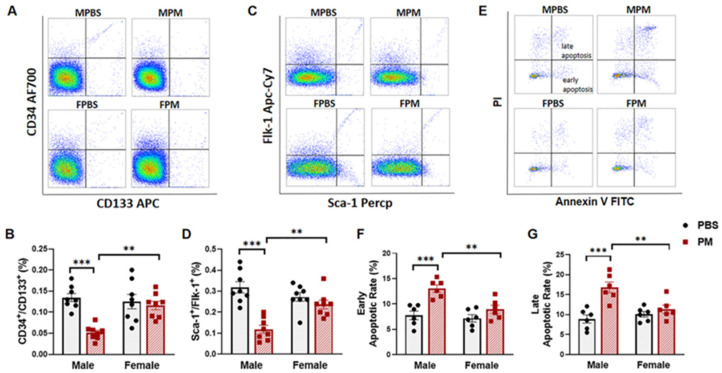
Figure 1.
PM exposure selectively decreased circulating EPC levels with an increased apoptosis rate in male mice. (A,C) White blood cells were stained with CD133 APC and CD34 AF700 or Sca-1 Percp and Flk-1 Apc-cy7 antibodies for flow-cytometric analysis of circulating EPCs (CD34+/CD133+) or (Sca-1+/Flk-1+), with summary data (B,D) showing that decreased levels of circulating EPCs were only observed in WT male mice with PM exposure (n = 8). (E) Annexin V and PI were used to incubate the blood cells for apoptosis analysis, which gated from EPCs (CD34+/CD133+), with summary data showing that both early (Annexin V+/PI-) (F) and late (Annexin V+/PI +) (G) apoptotic rates of EPCs in male mice with PM exposure were significantly increased as compared to the PBS control group and female mice (n = 6). MPBS: male mice with PBS treatment; MPM: male mice with PM exposure; FPBS: female mice with PBS treatment; FPM: female mice with PM exposure. ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001.