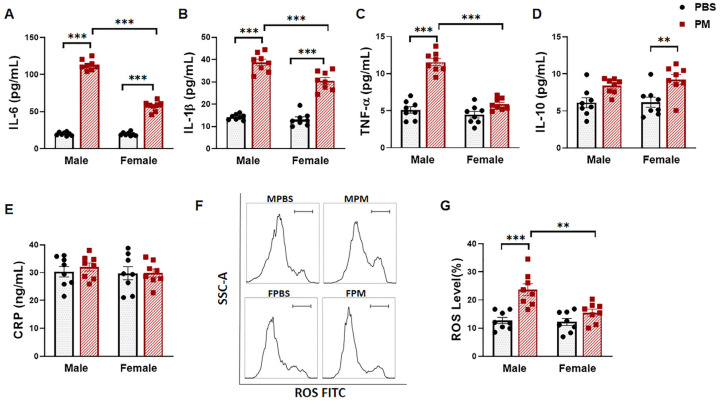
Figure 2.
PM exposure increased serum cytokines and ROS production. (A–C) Serum pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 (A) and IL-1β (B) were significantly increased in both male and female mice with PM exposure compared to the PBS control, while the serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in male mice were significantly higher than those in female mice. (C) pro-inflammatory TNF-α was significantly increased in male mice with PM exposure, but not in female mice. (D) Anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 was increased in female mice with PM exposure compared to the PBS control. (E) No significant change was observed in the level of serum CRP. (F) Flow cytometry analysis was used to detect the ROS in blood monocytes, with summary data (G) showing a significant increase in ROS production in male mice with PM exposure compared to the control group and female mice with PM exposure. MPBS: male mice with PBS treatment (n = 8); MPM: male mice with PM exposure (n = 8); FPBS: female mice with PBS treatment (n = 8); FPM: female mice with PM exposure (n = 8). ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001.