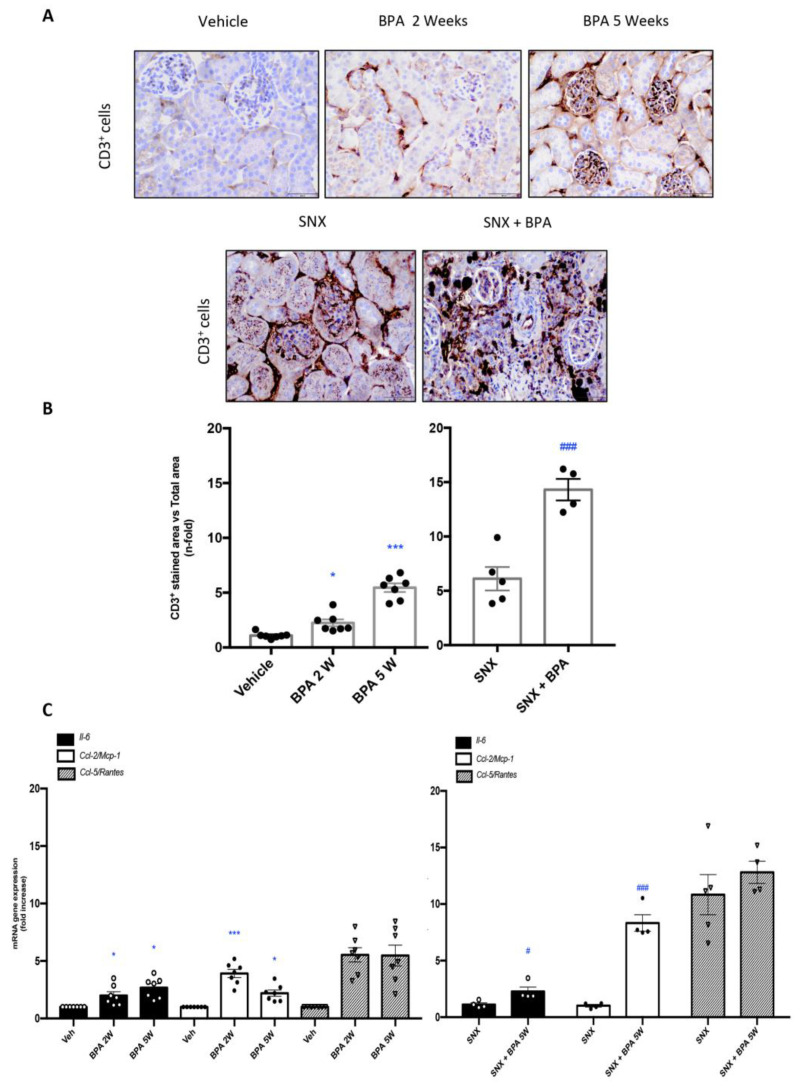
Figure 2.
Systemic chronic administration of BPA causes interstitial inflammatory cell infiltration in the kidney and increases renal expression of proinflammatory factors. Animals were intraperitoneal injected with 120 mg/kg/day BPA (5 days a week) or vehicle (corn oil) and sacrificed after 2 or 5 weeks. Some animals were subjected to subtotal nephrectomy (SNX), then treated or not with BPA and sacrificed after 5 weeks. (A) Paraffin-embedded kidney sections were stained with an anti-CD3+ antibody. Representative immunohistochemistry pictures identifying inflammatory T cell infiltration (CD3+ T lymphocytes). Magnification 200× (scale bar appears in lower right area of the image and represents 50 µm). (B) Immunohistochemistry staining quantification expressed as mean of stained area vs. total area ± SEM of 4–7 animals per group. (C) Gene expression of Il-6, Ccl-2 (Mcp-1) and Ccl-5 (Rantes) were evaluated by RT-PCR. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of 4–7 animals per group. * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001 vs. Vehicle, # p < 0.05; ### p < 0.001 vs. SNX. Comparison between SNX and SNX + BPA groups was performed using a parametric unpaired two-sided t test. The analysis of WT vs. BPA-treated groups was done by one-way ANOVA, followed by the Tukey HSD multiple comparison test.