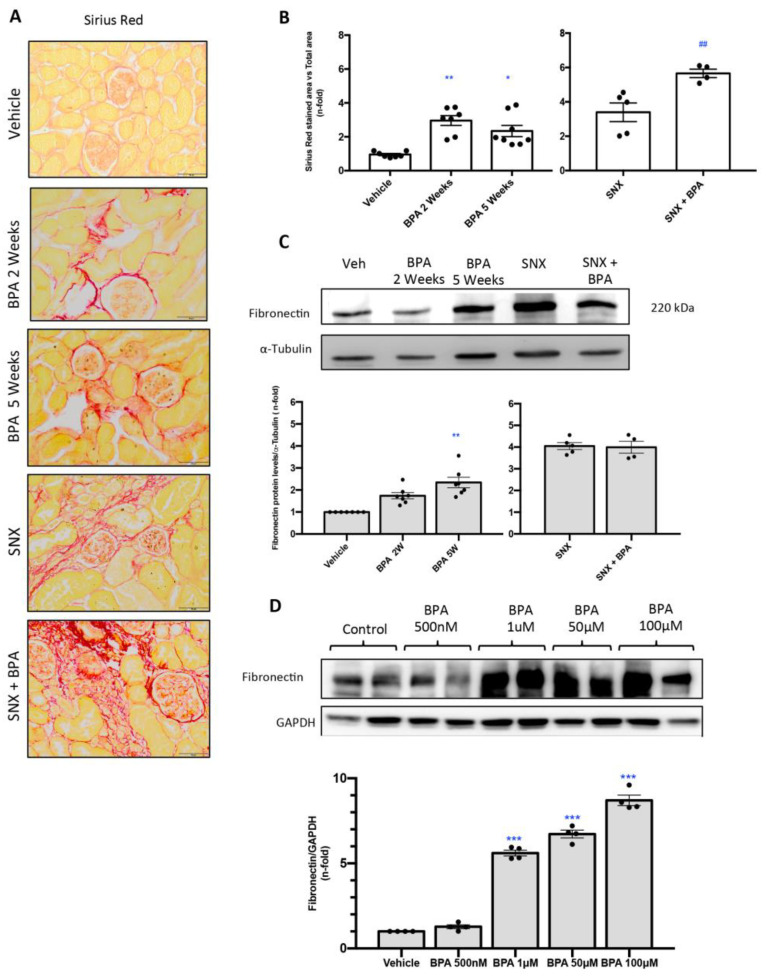
Figure 4.
Systemic chronic administration of BPA induces renal fibrosis in mice. Animals were intraperitoneal injected with 120 mg/kg/day BPA (5 days a week) or vehicle (corn oil) and sacrificed after 2 or 5 weeks. Some animals were subjected to subtotal nephrectomy (SNX), then treated or not with BPA and sacrificed after 5 weeks. (A,B) Collagen deposition was evaluated in paraffin-embedded sections by Sirius Red staining; quantification assessed the stained area vs. total area. (A) Figures show a representative picture from each group. Magnification 200×. (scale bar appears in lower right area of the image and represents 50 µm). (B) The quantification of Sirius Red staining. (C) Fibronectin protein levels were evaluated in total renal extracts by Western blot. Figures shows representative mice from each group and the quantification of the Western blot data. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of 4–7 animals per group. * p < 0.05 vs. control; *** p < 0.001 vs. control; ## p < 0.01 vs. SNX. (D) Treatment with BPA increases ECM proteins production in cultured renal cells. HK2 cells were treated with BPA at dose of 500 nM, 1, 50 and 100 μM for 48 h. Fibronectin levels were detected by Western blot. Figures shows representative experiment and the quantification of the Western blot. All data are presented as the mean ± SEM of 4 experiments, * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001 vs. Vehicle, ## p < 0.01; vs. BPA. Comparison between SNX vs. SNX + BPA groups was performed using a parametric unpaired two-sided t test. The analysis of WT vs. BPA-treated groups was done by one-way ANOVA, followed by the Tukey HSD multiple comparison Test.