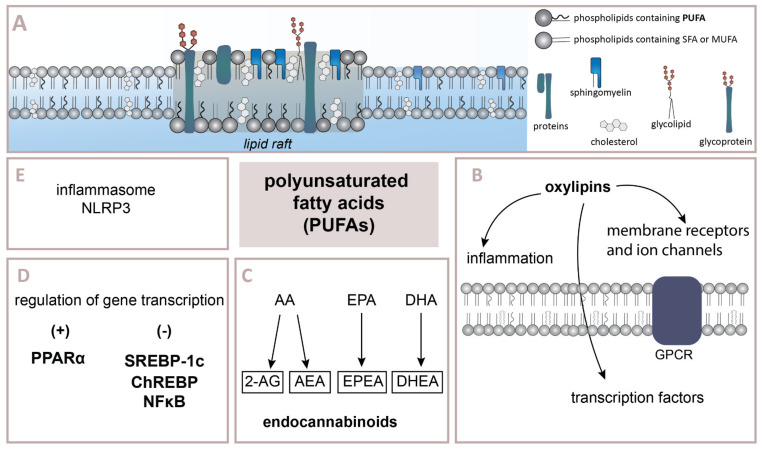
Figure 1.
Roles of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in the cell biology: A) PUFAs are components of cell membranes and disk membranes of rod outer segment; B) PUFAs incorporated in phospholipids are sources of oxylipins—the lipid mediators, crucial in inflammation, gene transcription regulation and influence membrane G Protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) and ion channels; C) Endocannabinoids 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), anandamide (AEA), eicosapentaenoyl ethanolamide (EPEA) and docosahexanoyl ethanolamide (DHEA) derived from arachidonic acid (AA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), respectively, affect inflammation; D) PUFAs control gene transcription through regulation of transcription factors such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) and sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c), carbohydrate-response element-binding protein (ChREBP), nuclear factor-κB (NFκB); E) N–3 PUFAs attenuate NLRP3 inflammasome activation. References: [60,61].