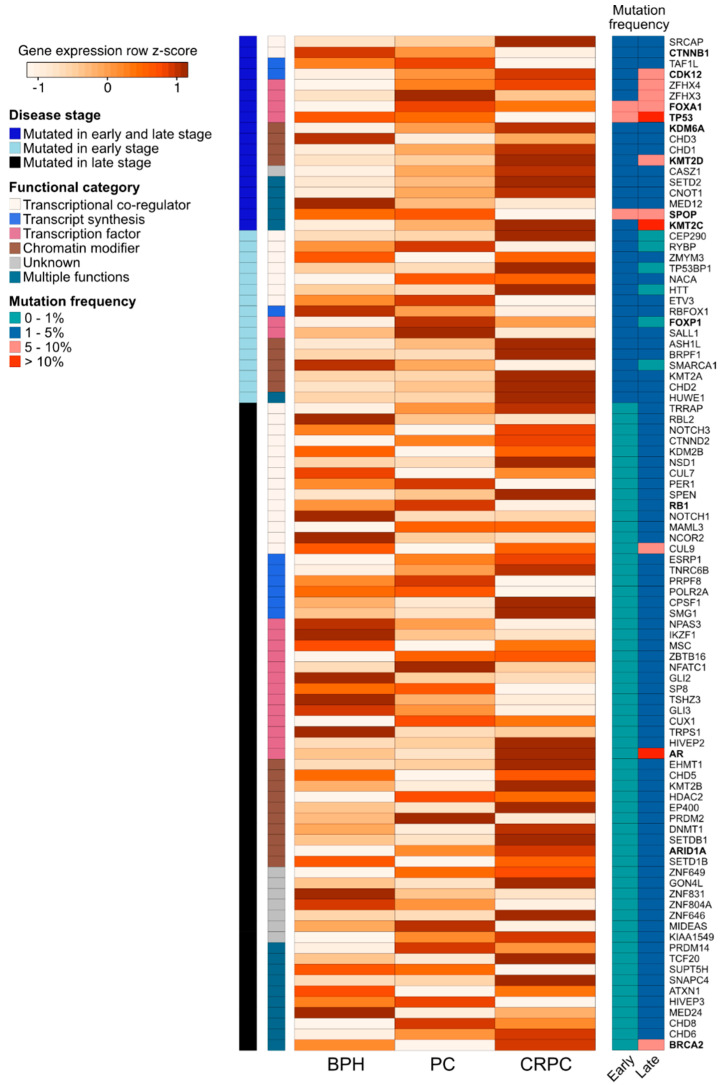
Figure 3.
Expression changes of 94 recurrently mutated genes coding for chromatin-associated proteins in prostate carcinogenesis and development of treatment resistance. Row-scaled log2 mean expression values for each gene (the rows) are shown in a heatmap for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), untreated prostate cancer (PC), and castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) patient samples. The names of frequently studied genes are shown in bold. Each row is annotated with the disease stage, in which the gene is found to be recurrently mutated (either early stage (PC), late stage (CRPC), or both early and late stage). The rows are also annotated with the functional category of each gene. On the right, two columns show the mutation frequency of the gene in early- and late-stage disease in four categories (0–1%, 1–5%, 5–10%, and >10%).