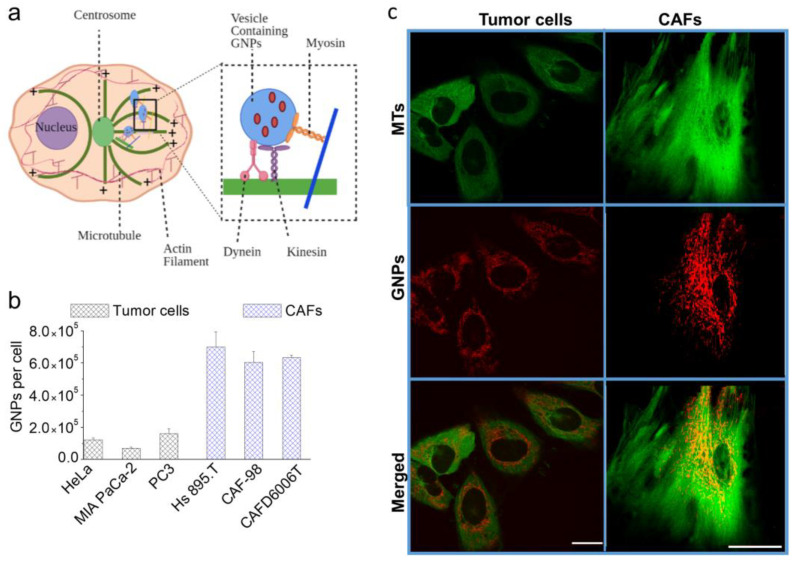
Figure 3.
GNP Uptake and Intercellular Transportation. (a) Schematic illustration displaying the transportation of vesicles containing GNPs within the network of microtubules (MTs). MTs are hollow tubes composed of tubulin dimers constructed into a linear chain of protofilaments. They are polar structures that have a fast-growing “positive” end and a slow-growing “negative” end. MTs emerge from an organelle in the center of the cell known as a centrosome or microtubule organizing center (MTOC), with the positive ends always directed outwards in the process of nucleation. Inset figure: the motor proteins, dynein and kinesin, support the transportation of vesicles along the MT network. (c) Confocal microscope images of tumors cells vs. CAFs, showing MTs alone in green (first row), GNPs alone in red (second row), and both MTs in green and GNPs in red merged (third row). (b) GNP uptake by tumor cells and CAFs in the absence of DTX. Scale bar = 20 μm.