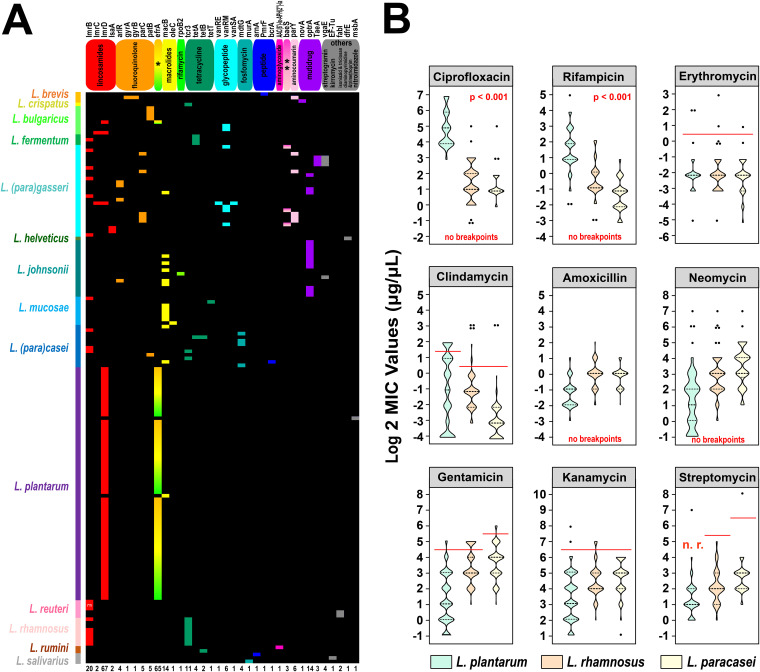
FIG 5.
Lactobacillus prophages are associated with antibiotic resistance. (A) The occurrence and distribution of ARGs across Lactobacillus prophages. Heat map illustrating the distribution of ARGs across 162 Lactobacillus prophages. The name order of prophages with ARGs (from top to bottom) is listed in Data Set S1, Tab3. The gene names and corresponding resistant antibiotics (types) are displayed at the top of the heat map, whereas the number of different ARGs is indicated at the bottom. *, efrA confers resistance to fluoroquinolone, macrolides, and rifamycin; **, baeS confers resistance to aminoglycoside and aminocoumarin. The names and host species (color bar) of the Lactobacillus prophages are indicated on the left side, whereas the gene copy numbers are listed on the right side. The code “*2” indicates that L. reuteri prophage FNXL81L1P2 carries two copies of lmrB. The ARG prediction results are provided in Data Set S1, Tab4. (B) Distribution of MIC values of 9 antibiotics for 115 L. plantarum, 121 L. paracasei, and 71 L. rhamnosus strains. The red lines represent microbiological breakpoints recommended by the EFSA. Statistical significance tests were performed using the nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis test.