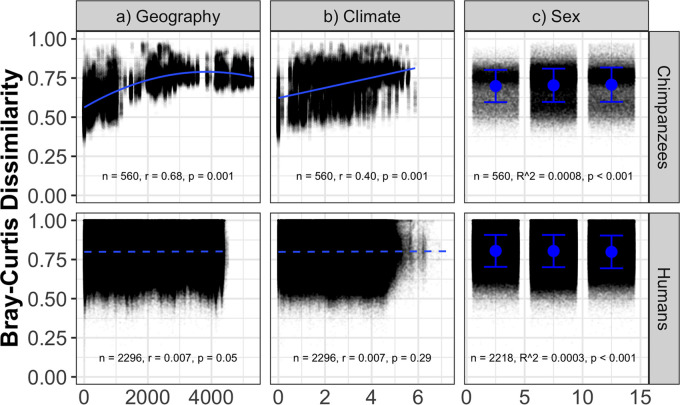
FIG 5.
Relationship between geographic distance (in kilometers), climate distance (Euclidean distance), sex (FF = female-female comparisons, FM = female-male comparisons, MM = male-male comparisons), and prokaryote (bacteria and archaea) community composition in chimpanzees and humans. For chimpanzees, a quadratic (geography) and linear (climate) trendline is shown, while for humans a dashed, nonsignificant, linear trendline is shown. Blue points and error bars represent means and standard deviations, respectively. Statistics are from Mantel tests (geography and climate) and analysis of variance (ANOVA) (sex). Note that while there were significant effects of sex on dissimilarity, and male-male comparisons were more dissimilar than female-female and female-male comparisons in chimpanzees, but less dissimilar in humans, the extremely small effect sizes in both species suggests sex does not structure the gut microbiome in either species.