FIG 1.
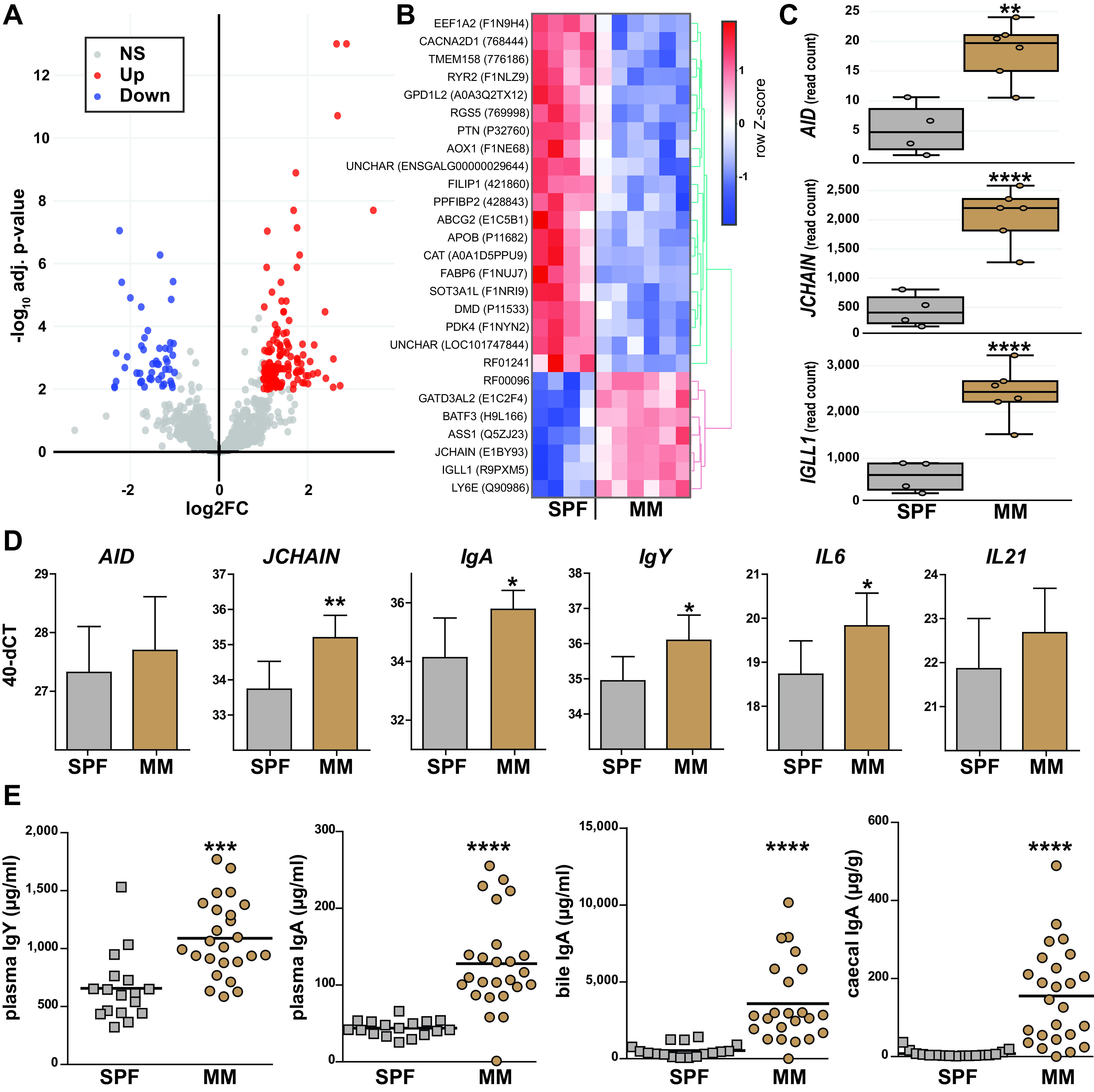
Host immune responses after fecal exposure. All readouts were generated at the age of 58 days. Chickens treated with maternal microbiota (MM) after hatch were compared to a control group kept under specific pathogen-free conditions (SPF). (A) Volcano plot of significantly and differentially regulated genes in cecal tonsil as assessed by RNA-seq (nSPF = 4, nMM = 6). (B) Heat map of the most significantly regulated genes (−log10 adjusted P value of >4). Uniprot accession numbers are indicated in brackets. (C) Read counts of the differentially expressed, immunologically relevant genes “activation induced cytidine deaminase” (AID), “joining chain” (JCHAIN), and “immunoglobulin variable region” (IGLL1). (D) qPCR analysis of immunologically relevant genes AID, JCHAIN, IgA, IgY, IL-6, and IL-21 (n = 6 in both groups). (E) Immunoglobulin concentrations as determined by quantitative ELISA (nSPF = 17 and nMM = 25 for IgY and IgA in plasma, and IgA in cecal content; nMM = 23 for IgA in bile). Adjusted P values for RNA-seq were obtained using the Wald test, including adjustment for multiple testing (Benjamini-Hochberg); P values for qPCR and ELISA were obtained by Mann-Whitney U test: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.
