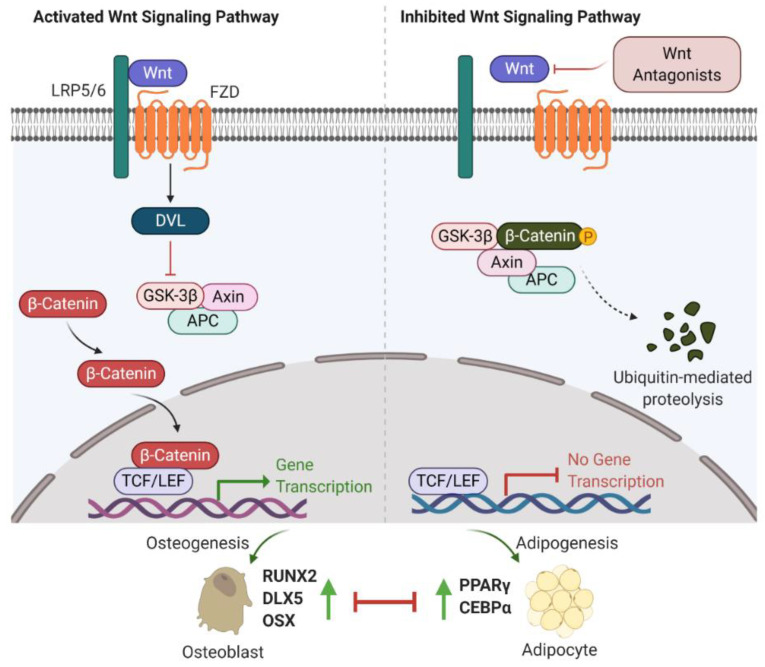
Figure 1.
Wnt/β-catenin signalling involved in bone or fat regulation. (Left) In case Wnt ligand is binding to co-receptor complex, β-catenin is released from the destruction complex composed of GSK-3β, Axin and APC. This allows β-catenin to be accumulated and translocated into nucleus. By interacting with TCF/LEF transcription factors, β-catenin activates the osteogenic-related gene transcription program and promotes osteogenesis and bone formation. (Right) In case Wnt ligand is not able to bind to its co-receptor complex (e.g., in the presence of Wnt antagonists (sFRP-1, WIF-1, DKKs and sclerostin)), β-catenin is sequestered by the degradation complex, phosphorylated and subsequently degraded. Attenuated β-catenin enhances adipogenesis and marrow fat formation. Wnt: Wingless; LRP5/6: low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6; Frizzled: FZD; DVL: disheveled; GSK-3β: glycogen synthase kinase 3β; APC: adenomatous polyposis coli; TCF/LEF: T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor; RUNX2: runt-related transcription factor 2; DLX5: distal-less homeobox 5; OSX: osterix; PPARγ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; C/EBPα: CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α.