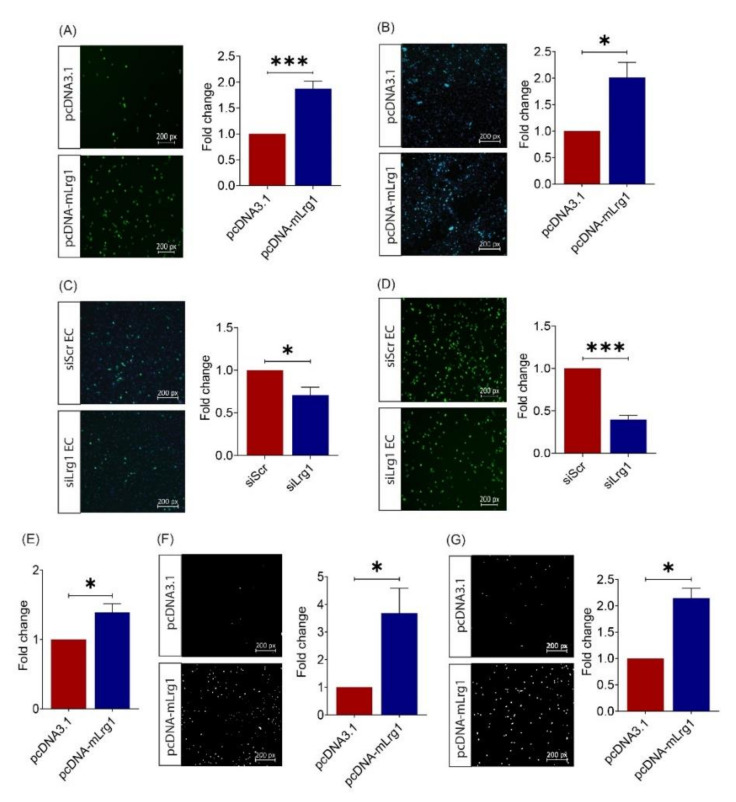
Figure 4.
Lrg1 promotes B16F10 cell invasiveness in vitro. (A) Representative images and quantitative analysis of the number of CMFDA-positive Lrg1 overexpressing or control B16F10 cells adhered to the HPMEC monolayer. (B) Representative images and quantitative analysis of the number of CMFDA-positive Lrg1 overexpressing B16F10 cells that migrated through the HPMEC monolayer. (C) Representative images and quantitative analysis of the number of CMFDA-positive B16F10 cells adhered to the HPMECs subjected to siRNA-mediated LRG1 knockdown. (D) Representative images and quantitative analysis of the number of CMFDA-positive B16F10 cells that migrated through the HPMECs subjected to siRNA-mediated LRG1 knockdown. (E) Quantitative analysis of Lrg1 overexpressing or control B16F10 cells adhered to fibronectin. (F) Representative images and quantitative analysis of invaded Lrg1 overexpressing and control B16F10 cells using the Matrigel invasion assay. (G) Representative images and quantitative analysis of migrated Lrg1 overexpressing or control B16F10 cells in Transwell. Migrated and invaded cells are labelled by DAPI. All images are representative. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. of three independent experiments. Statistical analyses were performed via two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test. * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001.