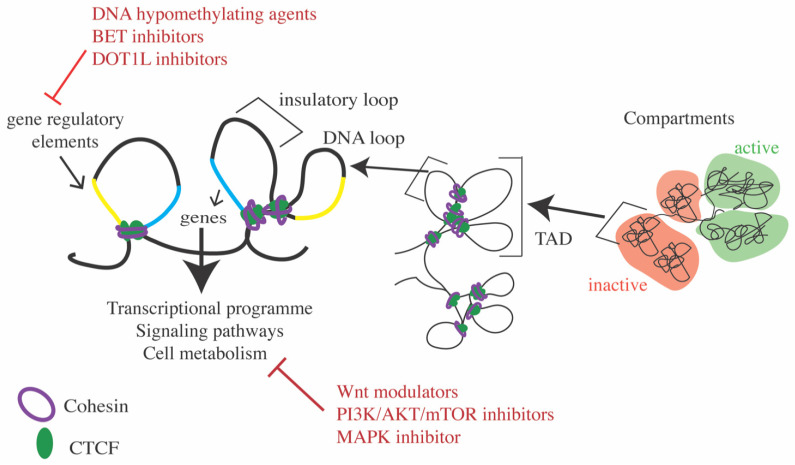
Figure 2.
Cohesin’s role in the hierarchical 3-dimensional organization of the genome. Cohesin association with DNA during interphase is required for formation of DNA loops and organization into TADs. DNA loops allow genes to either connect to their regulatory elements (enhancers) or insulate them from ectopic connections. TADs based on transcription and epigenetic modifications segregate into active and inactive compartments. Cohesin mutation can result in aberrant DNA loops, which leads to transcriptional dysregulation. Pharmacological agents that modulate the epigenetic modifications at gene regulatory elements or directly target gene transcription and associated signaling can be used to interfere with the aberrant gene transcription observed in cohesin mutant cells.