Figure 1.
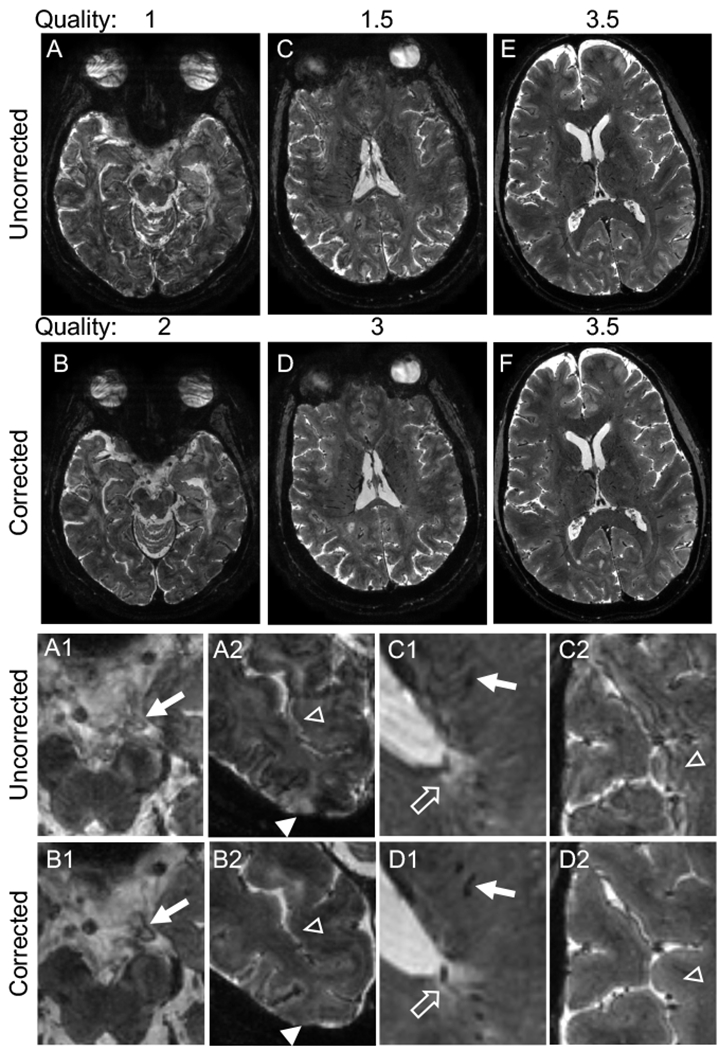
Navigator-guided motion and B0 correction improves the quality of T2*-weighted images. (A–D) Examples of uncorrected scans with a low-quality score (average of 2 ratings: 1 (A) and 1.5 (C)), which improved to 2 (B) and 3 (D) respectively after correction. (E–F) Example of a higher quality uncorrected scan (average rating 3.5) and corresponding corrected image with equal quality. All images are in the axial plane. Images in the bottom two rows are magnified portions of the images from the top rows. Correction improves visualization of vasculature (A1 vs. B1, C1 vs. D1, arrows) and clarity of the border of white matter lesions (C1 vs. D1, unfilled arrows). Correction also eliminates hyperintense artifact in the cortex (A2 vs. B2, filled arrowheads) and alternating hyperintense/hypointense artifact along the cortex (A2 vs. B2, C2 vs. D2, unfilled arrowheads), with resulting improvement in clarity of the cortex-white matter border (C2 vs. D2). Quality ratings: 1 – severe motion artifacts, 2 – moderate motion artifacts, 3 – minimal motion artifacts, 4 – no motion artifacts.
