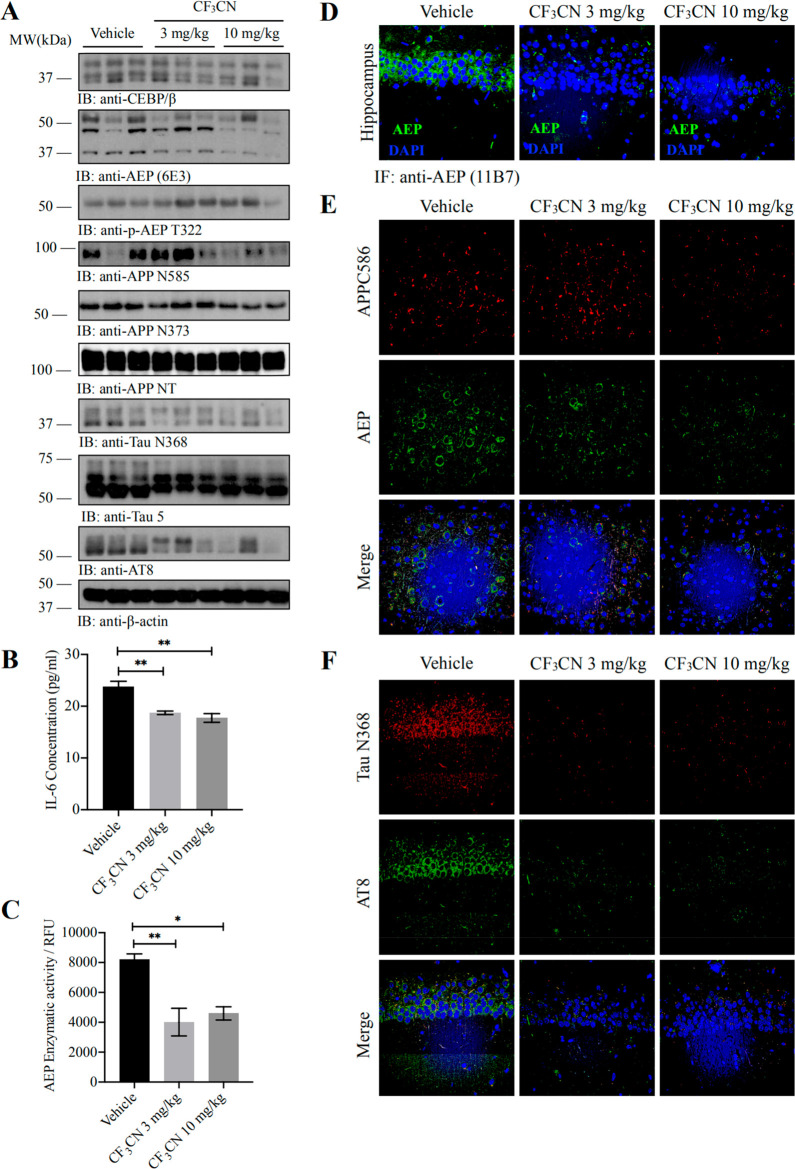
Figure 6.
CF3CN alleviates inflammation, inhibits AEP activation, and reduces the concentrations of AEP-derived APP fragments and Tau fragments. (A) Western blot showing the processing of APP and Tau by AEP. CF3CN significantly inhibited AEP activation by phosphorylation of AEP T322, which attenuated Tau and APP cleavage. (B) Pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 was determined by ELISA kit. Chronic CF3CN treatment significantly decreased the IL-6 production in mice brains compared with that of the age-related vehicle-treated mice (n = 5 in each group, data are shown as mean ± SEM **p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA). (C) AEP enzymatic activity analysis (n = 5 in each group, data are shown as mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with vehicle-treated mice brains, one-way ANOVA). (D) CF3CN repressed AEP expression levels in 5xFAD mice. Immunofluorescence showing the presence of AEP positive cells in hippocampus of both vehicle- and CF3CN-treated mice (scale bar, 50 μm). (E) CF3CN inhibits AEP activation and reduces delta-secretase-derived APP fragments. Immunofluorescence staining of cortex from 5xFAD mice brains with AEP antibody (green), cleaved APP C586 fragment antibody (red), and DAPI (blue). (F) CF3CN inhibits AEP activation and reduces delta-secretase-derived Tau fragments. Immunofluorescence staining of cortex from 5xFAD mice brain with cleaved Tau N368 fragment antibody (red), AT8 antibody (green), and DAPI (blue).