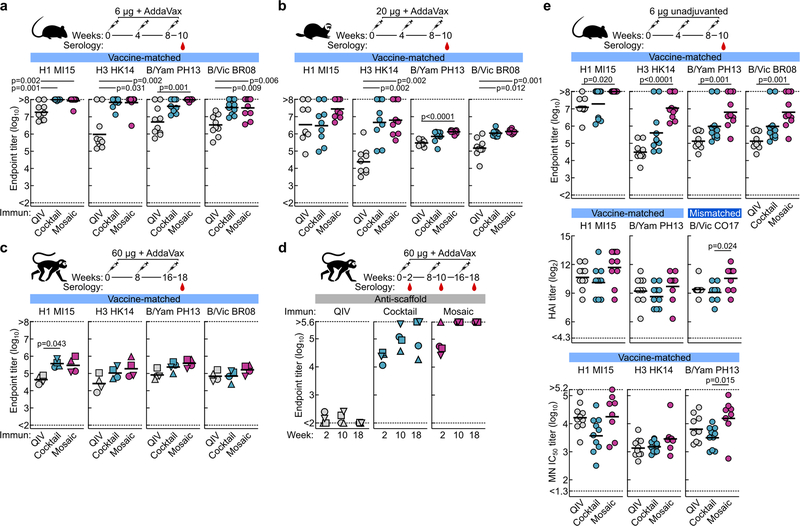
Extended Data Fig. 4 |. Vaccine-elicited antibody responses against vaccine-matched antigens.
HA-specific antibody titers in immunized mice (a), ferrets (b), and NHPs (c). Immunization schemes are shown at the top of each panel. All immunizations were given intramuscularly with AddaVax. Groups of BALB/cJ mice (N = 10), Finch ferrets (N = 9), and rhesus macaques (N = 4) were used in each experiment. ELISA antibody titers are expressed as endpoint dilutions. Each symbol represents an individual animal and the horizontal bar indicates the geometric mean of the group. Individual NHPs are identified by unique symbols. d, Antibody responses against unmodified I53_dn5 nanoparticles lacking displayed HA. Immunization scheme is shown at the top of the panel. Groups of NHPs (N = 4) were immunized three times with either QIV, qsCocktail-I53-dn5, or qsMosaic-I53_dn5 with AddaVax at weeks 0, 8 and 16. Serum samples were collected 2 weeks after each immunization and tested for ELISA binding antibody against unmodified I53_dn5 particles. Antibody titers are expressed as endpoint dilutions. Individual NHPs are identified by unique symbols. The immunization study was performed once. e, Antibody responses against vaccine-matched antigens and viruses elicited by unadjuvanted vaccines in immunized mice. Immunization scheme is shown. All immunizations were given intramuscularly. Groups of BALB/cJ mice (N = 10) were used. HA-specific ELISA binding antibody (top), hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) (middle), and microneutralization titers (bottom) in immune sera are shown. Microneutralization titers are reported as half maximal inhibitory dilution (IC50). Each symbol represents an individual animal and the horizontal bar indicates the geometric mean of the group. Statistical analysis was performed using nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons. All animal experiments except for NHP were performed at least twice and representative data are shown.