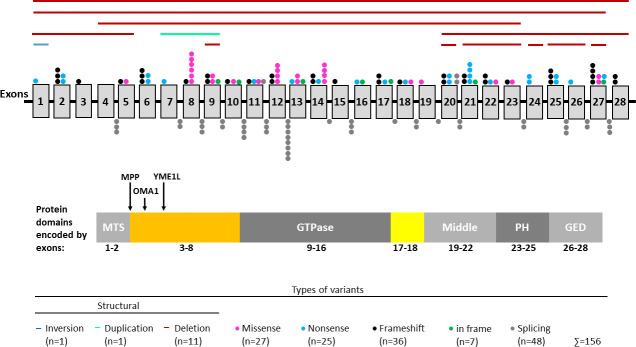
Fig 1. Distribution of OPA1 variants.
Shown is the isoform that lacks the alternative exons 4b and 5b (NM_015560.2). Exons are represented by grey vertical boxes. Note that exons and intervening intronic sequence (represented by black horizontal line) are not drawn to scale. Each distinct variant observed in our cohort is represented by a single distinct color coded dot above the respective exon or below the respective intron. Structural variants are indicated by horizontal lines above the exons. Shown below the gene structure is the protein with its most important domains including a GTPase domain, a middle domain that is involved in oligomerization, a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain and a GTPase effector domain (GED). The peptide encoded by exons 17–18 (shown in yellow) forms a long helix that connects the GTPase domain and the middle domain. Exons 1 and 2 encode a mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) which is cleaved by the mitochondrial processing peptidase (MPP). The N-terminal region encoded by exons 3–8 (shown in orange) does not include specific domains but comprises mitochondrial proteolytic cleavage sites for the mitochondrial processing peptidases OMA1 and YME1L. Protein structure was adapted from Li et al., 2019 [109].