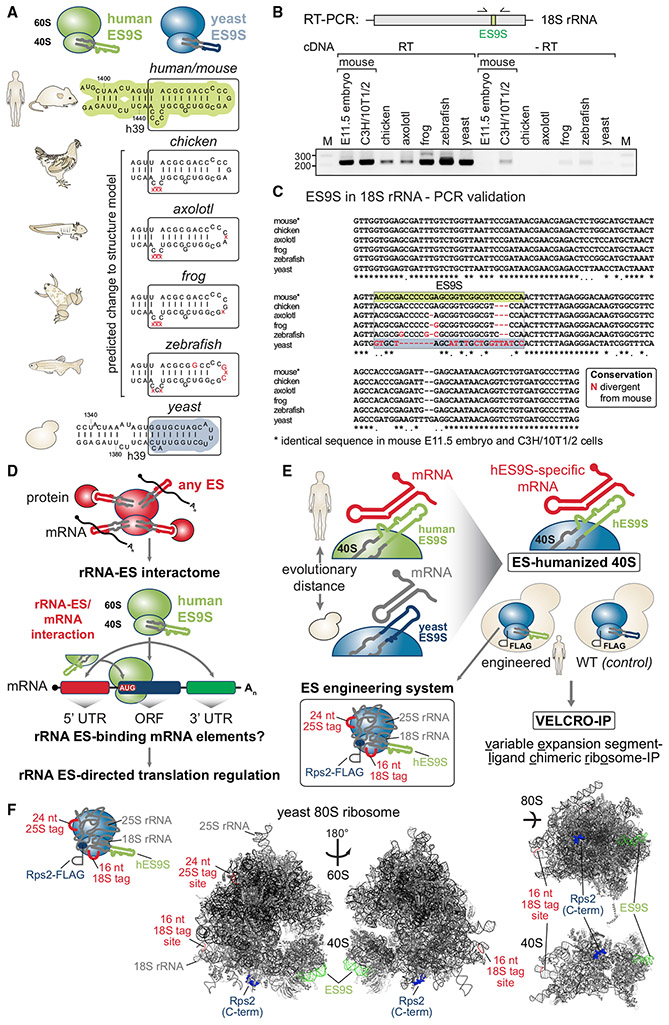
Figure 1. Confirmation of interspecies sequence variation of the ES9S 18S rRNA region.
(A) Secondary structure models of the human (H. sapiens) and baker’s yeast (S. cerevisiae) 18S rRNA region containing ES9S, highlighted in green and blue, respectively. Predicted structural changes in ES9S because of species-specific variation in sequence. Sequence divergence from the human/mouse ES9S are annotated in red. Secondary structure models of ES9S were predicted using Vienna RNAfold (http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at) and visualized using VARNA (http://varna.lri.fr). See also Figure S1.
(B) Schematic of the RT-PCR analysis of the ES9S region using cDNA generated from total RNA from six species (E11.5, stage E11.5 FVB mouse embryo; chicken, Gallus gallus; axolotl, Ambystoma mexicanum; frog, Xenopus laevis; zebrafish, Danio rerio; yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and primers specific for the 18S rRNA region containing ES9S (see Table S3).
(C) Multiple sequence alignment of the variable ES9S region in highly conserved 18S rRNA. PCR product sequencing after RT-PCR spanning the ES9S region with the outer primers in (B) for six species confirms the annotated species-specific ES9S sequence. Nucleotides divergent from human/mouse ES9S are highlighted in red.
(D) Concept of revealing extended rRNA ES interactions on the ribosome with mRNAs or proteins. This enables analysis of ES9S interactions, the ES of choice in this work, via the 40S ribosomal subunit with positional resolution to identify and map ES9S binding mRNA elements underlying unexplored ES-directed translation regulation.
(E) Schematic of the VELCRO-IP (variable expansion segment-ligand chimeric ribosome-IP) approach to investigate ES-mediated translation regulation through mRNA interactions. Generating FLAG-tagged humanized ribosome strains that exclusively contain human ES9S in yeast 18S rRNA and tagged WT control yeast strains in parallel enables an ES engineering system that contains rRNA and protein tags and allows the manipulation of any ES.
(F) Mapping of the components of the ES engineering system onto the cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the yeast 80S and 40S ribosome (PDB: 4V6I). The sites of rRNA tag insertion,the last 10 amino acids of the C terminus of Rps2/uS5, and ES9S are highlighted according to the schematic representation.