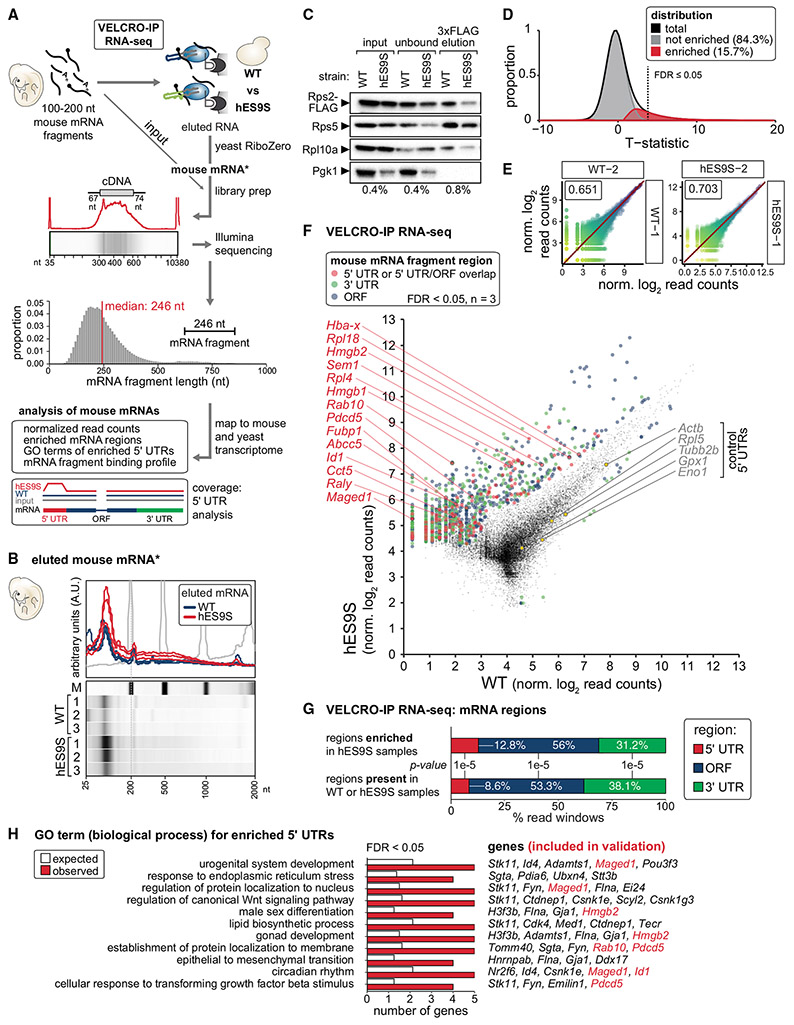
Figure 4. VELCRO-IP RNA-seq identifies global ES-mRNA interactions with positional resolution on mRNAs.
(A) For VELCRO-IP RNA-seq, mRNA was isolated from stage E11.5 mouse embryos, fragmented, and used as input. Eluted and yeast rRNA-depleted RNA obtains ribosome-bound mouse mRNA fragments for library preparation and Illumina sequencing, including the mRNA fragment input for reference. The distribution of mRNA fragment lengths for all sequenced libraries is plotted with a median fragment length of 246 nt. All reads were mapped to the mouse and yeast transcriptomes, and only reads exclusively mapping to mouse mRNAs were further analyzed.
(B) Eluted and yeast rRNA-depleted mouse RNA from three independent replicates of WT and hES9S VELCRO-IP experiments were analyzed on an mRNA Pico Chip (Agilent) on a Bioanalyzer (Agilent) as in Figure 3F. See Figure S3D.
(C) WB analysis as in Figure 3C to monitor efficient IP of 40S ribosomes after VELCRO-IP. A representative experiment of n = 3 is shown.
(D) Kernel density of the distribution of t-statistics for the test of differential enrichment of mRNA fragments bound to hES9S versus WT ribosomes is plotted in black. Empirical estimates of the decomposition of the test statistics distribution to null and non-null tests are plotted in gray and red, respectively. The dotted line indicates local FDR of 0.05.
(E) Comparison of individual VELCRO-IP RNA-seq samples (three replicate samples per hES9S and WT). Scatterplots of normalized log read counts, colored by expression level. Pearson correlation coefficients are shown in the top-right boxes. See Figure S4A.
(F) RNA-seq results of independent replicates (n = 3) for each WT and hES9S sample. Normalized log read counts are presented for WT and hES9S-enriched mouse mRNA fragments. Fragments (FDR < 0.05) are colored according to the mRNA region to which they map (see legend): 5′ UTR or overlapping 5′ UTR/ORF (red), 3′ UTR (green), and ORF (blue). Mouse genes are labeled for which enriched fragments in the 5′ UTR and/or 5′ region of the ORF were identified and for which 5′ UTR validation experiments were performed. Five control 5′ UTRs are marked that are equally bound to both WT and hES9S 40S subunits and served as negative controls. See Figure S4B and Table S4.
(G) Analysis of regions mapping to 5′ UTR, ORF, or 3′ UTR in hES9S-enriched samples compared with their presence in WT or hES9S samples, each n = 3, expressed as the percentage of total read windows identified. The indicated p value is calculated by a chi-square test.
(H) Gene Ontology (GO) analysis for the biological process of 87 5′ UTR regions (FDR < 0.05, n = 3) enriched by hES9S. Displayed are the expected and observed frequency of genes for the significant terms (FDR < 0.05) (expressed mRNA regions were used as the background population; see STAR Methods for details of the thresholds used). See Figure S5 for GO terms of ORF, 3′ UTR, and full mRNA (all regions), as well as Table S5.