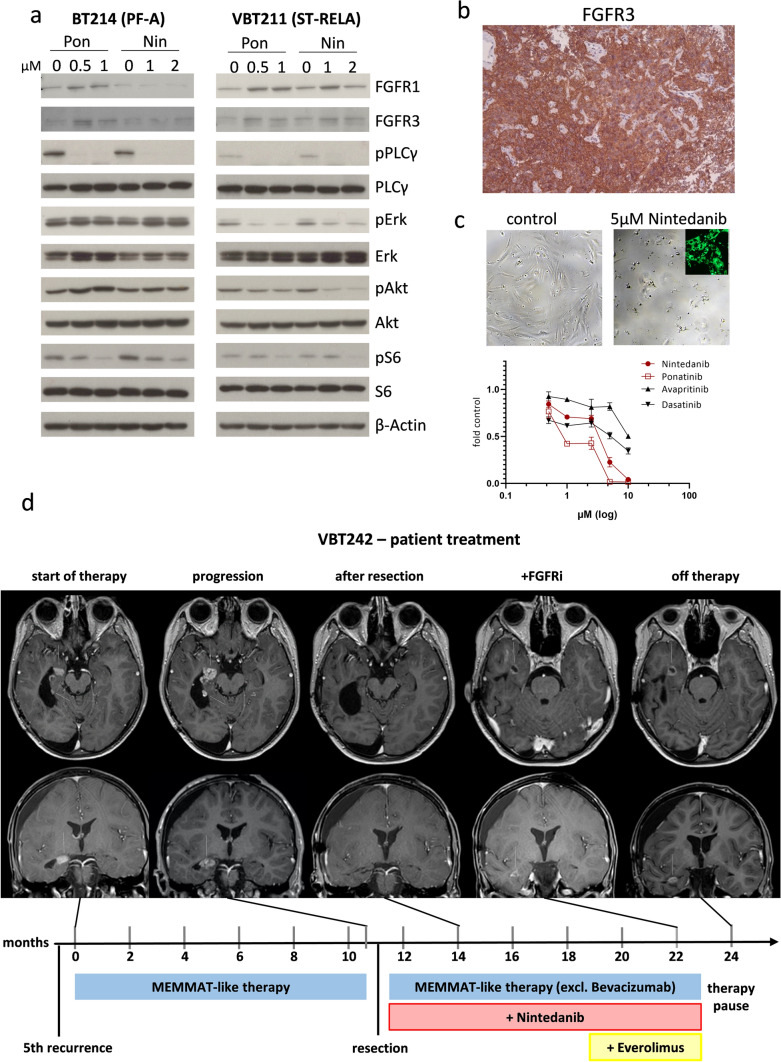
Fig. 6.
Targeting FGFR inhibits MAPK and PI3K pathway activation, induces differentiation and is applicable in the clinic. a Effects of long-term treatment (24 h) with ponatinib (Pon) and nintedanib (Nin) on FGFR1 and FGFR3, on PLCγ, MAPK and PI3K signaling activation (indicated by changes in the phosphorylation status) in PF-A (BT214) and ST-RELA (VBT211) cells was analyzed by Western blot. ß-actin served as a loading control. b Immunohistochemical staining of FGFR3 in tissue section of VBT242 at resection prior to FGFRi treatment is depicted. c Cell viability of VBT242 upon treatment with the FGFR inhibitor nintedanib and the FGFR/multikinase inhibitor ponatinib, compared to avapritinib and dasatinib targeting PDGFRA and Src, respectively, was determined and is expressed as dose–response curve. Representative pictures at 72 h nintedanib exposure (5 µM) are depicted above. Intracellular accumulation of the drug is verified by the green fluorescence photomicrograph. d Course of disease and treatment regimen in a patient suffering from ST-RELA EPN (corresponding to the VBT242 model). Time zero represents the time when the patient was admitted to our center for treatment of the 5th recurrence. The timeline indicates therapeutic interventions and clinical course. MEMMAT-like therapy was carried out as previously published [50] and NCT01356290. Tumor manifestations are indicated with white arrows on axial und coronal contrast-enhanced T1-weighted magnetic resonance images (MRI) at indicated time points. FGFRi FGFR-inhibitor