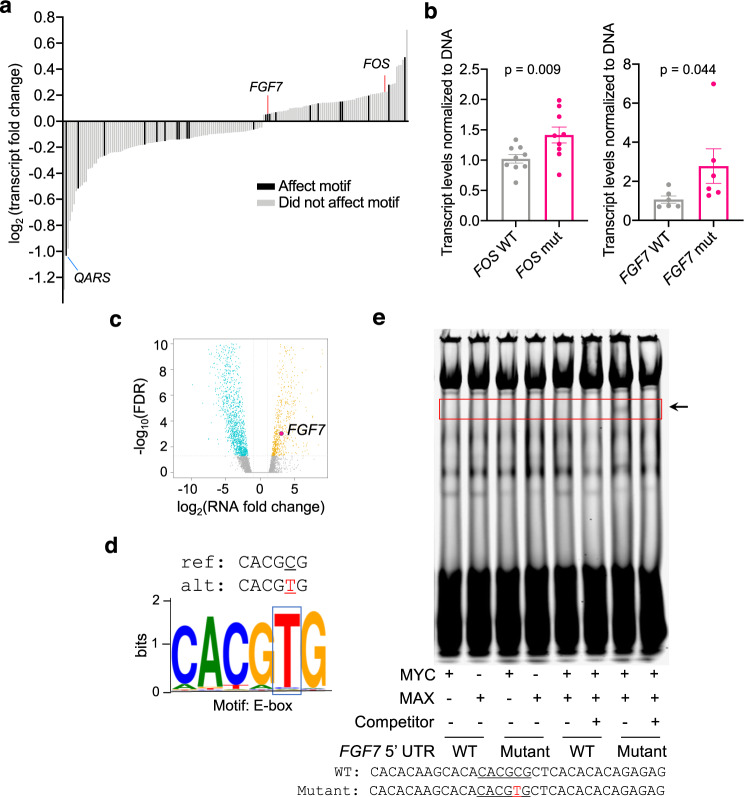
Fig. 4. PLUMAGE reveals how somatic 5′-UTR mutations affect mRNA transcript levels.
a 5′-UTR mutations that significantly affect mRNA transcript levels (Mann–Whitney U test, FDR < 0.1) and magnitude fold change compared to unmutated 5′-UTR (Supplementary Data 6d). A proportion of mutations also impact a known DNA-binding element, indicated by black bars. b qPCR validation of the FOS (chr14: 75745674, C -> G) and FGF7 (chr15: 49715462, C -> T) 5′-UTR mutations identified by PLUMAGE. WT (represented by gray dots) and mutant (represented by pink dots) 5′-UTRs were cloned into a luciferase reporter construct and transduced into PC3 prostate cancer cells. Luciferase transcript levels were then normalized to luciferase DNA (n = 9 biological replicates for FOS WT and mutant, mean ± s.e.m. Student’s t test; n = 6 biological replicates for FGF7 WT and mutant, data are presented as mean ± s.e.m., one-sided Student’s t test). c RNAseq volcano plot of all significantly up- and down-regulated mRNAs in the human prostate cancer PDX LuCaP 81 (FDR < 0.1). Each dot represents the transcript fold change of a 5′-UTR mutation in LuCaP 81; turquoise dots are 5′-UTR mutations that significantly downregulate transcript expression of its specific mRNA (FDR < 0.1), yellow dots are 5′-UTR mutations that significantly upregulate transcript expression of its specific mRNA (FDR < 0.1). Within this PDX, FGF7 exhibits a 5′-UTR mutation (indicated by pink dot) at chr15: 49715462, C -> T that is associated with an increase in FGF7 transcript levels. d The FGF7 5′-UTR mutation introduces a thymidine at position chr15: 49715462, which transforms the CACGCG sequence into an E-box motif (CACGTG). Mutated nucleotide is represented in red. e Representative EMSA using the WT vs mutant FGF7 5′-UTR. Labeled probe sequences (33-bp) containing the E-box sequence generated by the mutation in the 5′-UTR of FGF7 and the wild-type sequence are shown. Mutated nucleotide is represented in red. Binding of MYC:MAX heterodimer protein complex is observed only with the mutated oligonucleotide probe containing the E-box sequence. Binding of the labeled oligo can be abolished using an unlabeled competitor. Source data are provided as a Source data file.