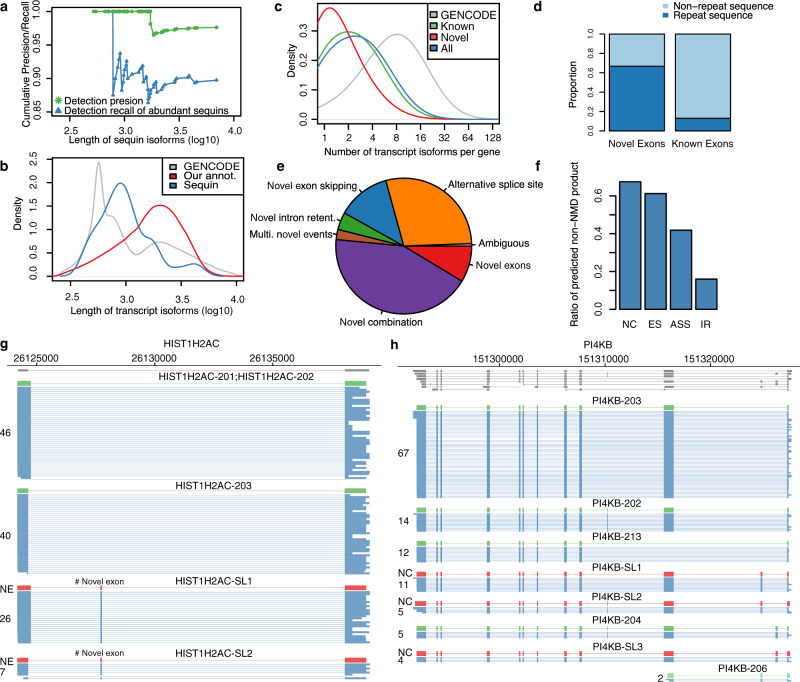
Fig. 2. FulQuant method accurately identifies transcript isoforms in iPSC-CMs.
a Length dependent precision (green) and recall (blue) of the FulQuant method as estimated using all or the most abundant 50% synthetic sequin controls. b Length distribution of transcripts in GENCODE, of our identified isoforms, and of the sequin controls. a, b are vertically aligned with the same x axis to illustrate the relevance of the accuracy estimated by sequins on human transcripts. c Distribution of number of isoforms per gene based on GENCODE comprehensive annotation and the transcripts identified in this study (divided into Known, Novel, and All). d Proportion of known exons that contain repeat sequences compared to the proportion of identified novel exons. e Percentages of novel transcripts isoforms by the types of novel splicing events: novel exon (NE), novel intron retention (IR), novel alternative splice sites (ASS), novel exon skipping (ES), and unannotated combinations of known exons (NC). Ambiguous transcripts are those with alignment issues. f Ratio of predicted non-NMD product in each novel transcript categories. g, h Examples of genes with unannotated combinations of known exons and novel exon, respectively. Known isoforms in the comprehensive GENCODE annotation are shown in gray track. Isoforms with <5 reads are not shown. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.